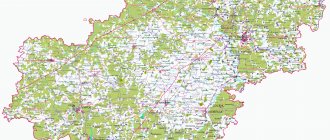
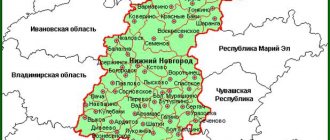
In the south-west of the Central part of Russia there is a small subject of the Russian Federation - the Lipetsk region. This is the smallest region in the Central Black Earth economic region of the country. Using a satellite map of the Lipetsk region, you can see that the following areas border the region:
- Ryazan;
- Voronezh;
- Kursk;
- Tambovskaya;
- Tula;
- Orlovskaya.
The region's territories are not very densely populated. This is explained by the fact that in the region a large amount of land is occupied by numerous rivers and reservoirs, most of which belong to the Don basin. The main rivers of the region can be seen on the map of the Lipetsk region by region:
- Voronezh;
- Matyra;
- Beautiful Mecha;
- Standing Cassock;
- Pine.
A number of rivers belong to the Volga basin and are located in the northeastern part of the region. The lands of the region are black earth. Since ancient times, the population living here has been engaged in arable farming and growing agricultural crops.
The formation of the region as a subject of the Russian Federation occurred in the middle of the last century, when several districts around the city of Lipetsk were united. Natural objects, industrial zones, streets, houses and districts on the map of the Lipetsk region can be studied by zooming in and moving around the online service using the mouse.
Lipetsk is a densely populated city in the central Black Earth Region.
Over the past ten years, there has been a significant outflow of the population, but people themselves say that many return here after a long stay in Moscow, where they are looking for decent earnings. Most Lipetsk residents need to move to the capital, with its attractive prospects, to save money to buy a home. Meanwhile, there are many problems with housing and housing and communal services. The list is quite long, but it can be boiled down to a few main difficulties.
In some areas, the population density is so high that utility services simply cannot cope with the maintenance of homes. Lipetsk is located in a climatic zone characterized by a sharp onset of winter. A large number of cars and sudden precipitation often lead to transport collapse. An insufficient number of snow removal equipment cannot provide the desired benefit. Yard cleaning is often completely forgotten.
The wear and tear of the heating mains regularly used by residents forces repair and restoration work to be carried out twice a year. Moreover, sometimes services do not do their job at all, which causes the infrastructure to suffer even more. Throughout the Lipetsk region there are not enough kindergartens and schools. Local authorities have taken many actions in 2021 to correct the problem. So far, this only works in relation to new microdistricts where the construction of corresponding municipal institutions is underway. Electronic child registration plays a useful role, allowing residents to determine the child's position in the queue. There is also compensation, which is 5,000 rubles. — such a payment awaits everyone whose children were unable to get into kindergarten and were forced to continue to wait (valid for children from 3 to 6 years old).
Economy and industry of the Lipetsk region
The economic potential of the region consists of industry and agriculture. The region is located in the black earth zone, so active crop production is carried out here. In total, there are about 300 agricultural enterprises in the region that grow fruits and berries, grain crops, and breed meat and dairy animals.
Using Yandex maps of the Lipetsk region, you can get an idea of the location of industrial zones in the region. The main enterprises are located in Lipetsk and its vicinity. The diversified industrial complex of the region is represented by such areas as:
- metallurgy;
- mechanical engineering;
- electric power industry;
- light;
- food
On the map of the Lipetsk region you can see in detail where the largest enterprises that produce are located:
- granulated sugar;
- refrigerators and freezers;
- black rolled metal;
- juices;
- pasta;
- steel products.
Construction is also a developed industry. In the Lipetsk region, several hundred thousand square meters of housing are built annually by local construction companies, new facilities appear, roads and bridges are built.
Yelets is a small town
Yelets never aspired to become big. This settlement is specially created for tourists, so local authorities are trying to develop the infrastructure. The authorities are undertaking various programs that are designed to regulate tariff rates for:
- gas;
- water;
- electricity supply;
- housing maintenance;
- improvement of housing stock.
The results generally please the townspeople, who receive playgrounds and landscaped courtyards. Moreover, for this they do not have to overpay significantly, since there are still the same well-thought-out tariffs.
There are practically no traffic jams in the city. However, due to the one-way traffic that prevails here, you may encounter slight congestion. The city has a sufficient number of schools and kindergartens, but many of them are paid. Residents of Yelets are employed in trade enterprises. Nowadays, catering establishments often begin to open in the city. Therefore, there is enough work, but finding employment can be difficult.
Gryazi - industrial town
Mechanical engineering has become a city-forming industry for the city of Gryazi. The settlement plays an important role, being a major railway junction connected with Moscow, Rostov, Orel and Volgograd.
The population is provided with work, but has problems with infrastructure. Housing and communal services require serious improvement measures. The city has kindergartens, private schools, and an art gymnasium. The general situation in Gryazi is typical for any regional city that has a relatively good level of improvement. Young people often leave Gryazi to go to millionaires to look for education and work.
Lebedyan is a beautiful small town
The population is constantly declining; since 2011, there has been an outflow of more than 1,000 people. For the city, the authorities came up with an amazing solution considering the extremely small area.
In 1989, construction of the metro began. The initiator was Leonid Mulyarchik. With the support of local municipalities, he began digging a tunnel, which now reaches only 200 meters. However, experts confirmed that the structure is reliable, but now the metro is officially closed and blocked. Its construction continued until 2011. Lebedyan is characterized by a problem with a shortage of medical personnel, which applies to many settlements in Russia. There is a “Health” program here, but its implementation is at a mediocre level.
CITIES OF LIPETSK REGION
| Population (estimated as of January 1, 2009), thousand people: Lipetsk region total population - 1163.3 men - 528.3 women - 635.0 Lipetsk total population - 502.5 men - 227.7 women - 274.8 Yelets total population - 111.2 men - 50.1 women - 61.1 Population density (as of January 1, 2009), people per 1 km2: Lipetsk region - 48.4 Lipetsk - 1567.1 Yelets - 1709.7 | Administrative-territorial division of the Lipetsk region as of January 1, 2009 Districts - 18 Cities - 8 Intra-city districts, city districts - 4 Cities (number of inhabitants - estimate as of January 1, 2009, thousand people): Lipetsk - 502.5 Elets - 111.2 Gryazi - 46.4 Dankov - 22.2 Lebedyan - 20.7 Usman - 19.4 Chaplygin - 13.2 Zadonsk - 10.5 Territory area, thousand km2: Lipetsk region - 24.0 Lipetsk - 0.321 Yelets - 0.065 |
GROUPING CITIES BY PERMANENT POPULATION1)
| Total | including the number of inhabitants, thousand people | ||||||||||
| until 3 | 3 — 4,9 | 5 — 9,9 | 10 -19,9 | 20 — 49,9 | 50 — 99,9 | 100 — 249,9 | 250 — 499,9 | 500 — 999,9 | 1 million or more | ||
| Number of cities | |||||||||||
| 2008 | 8 | — | — | — | 3 | 3 | — | 1 | — | 1 | — |
| 2009 | 8 | — | — | — | 3 | 3 | — | 1 | — | 1 | — |
| Population, people | |||||||||||
| 2008 | 747354 | — | — | — | 43002 | 89688 | — | 112188 | — | 502476 | — |
| 2009 | 746134 | — | — | — | 43061 | 89325 | — | 111213 | — | 502535 | — |
| __________ 1) Estimate as of January 1. | |||||||||||
DISTRIBUTION OF POPULATION OF LIPETSK AND CITIES WITH POPULATIONS OVER 100 thousand people BY AGE GROUPS 1
)(thousands of people)
| Lipetsk | Dace | |||
| 2008 | 2009 | 2008 | 2009 | |
| Whole population | 502,4 | 502,5 | 112,2 | 111,2 |
| including those aged: | ||||
| younger than able-bodied | 70,8 | 70,7 | 15,5 | 15,4 |
| of which children aged 1-6 years | 27,1 | 28,0 | 5,9 | 6,1 |
| able-bodied2) | 325,6 | 323,5 | 69,9 | 68,9 |
| older than able-bodied | 106,0 | 108,3 | 26,8 | 26,9 |
| __________ 1) Estimate as of January 1. 2) Men 16-59 years old, women 16-54 years old. | ||||
SHARE OF LIPETSK AND CITIES WITH A POPULATION OVER 100 thousand people IN THE MAIN SOCIO-ECONOMIC INDICATORS
OF THE LIPETSK REGION in 2008
(percent)
| Lipetsk | Dace | |
| Population (est. January 1, 2009) | 43,2 | 9,6 |
| Average annual number of employees of organizations1) | 52,4 | 10,9 |
| Availability of fixed assets of organizations 2) (at the end of the year) | 71,73) | 7,2 |
| Volume of shipped goods of own production, work and services performed in-house by type of activity1): | ||
| mining | 59,3 | 11,7 |
| manufacturing industries | 81,9 | 1,9 |
| production and distribution of electricity, gas and water | 80,9 | 9,0 |
| Scope of work performed for the type of activity “Construction”1) | 85,4 | 5,2 |
| Commissioning of the total area of residential buildings | 53,3 | 8,9 |
| Retail trade turnover1) | 85,8 | 3,3 |
| Investments in fixed capital1) | 62,2 | 2,7 |
| __________ 1) For organizations not related to small businesses. 2) At full book value; for commercial and non-profit organizations (excluding small businesses). 3) Including funds of OJSC Gazprom. | ||
SOCIO-ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF LIPETSK AND CITIES WITH POPULATIONS OVER 100 thousand people
| Lipetsk | Dace | |||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2007 | 2008 | |
| POPULATION | ||||
| Population (end of year estimate), thousand people | 502,4 | 502,5 | 112,2 | 111,2 |
| Number of births per 1000 population | 9,7 | 10,2 | 9,6 | 9,9 |
| Number of deaths per 1000 population | 13,7 | 13,7 | 17,0 | 17,3 |
| Natural increase, decrease (-) per 1000 population | -4,0 | -3,5 | -7,4 | -7,4 |
| WORK | ||||
| Average annual number of employees of organizations1), thousand people | 185,1 | 178,3 | 37,2 | 37,1 |
| The number of unemployed citizens who applied for assistance in finding suitable work at government employment service institutions (at the end of the year), people | 1798 | 2280 | 881 | 918 |
| of them are recognized as unemployed | 1387 | 2006 | 815 | 842 |
| LIVING STANDARD OF THE POPULATION AND SOCIAL SPHERE | ||||
| Average monthly nominal accrued wages1), rub. | 13703,4 | 17157,8 | 9225,1 | 11420,7 |
| Average size of assigned pensions, rub. | 3653,7 | 4523,9 | 3559,4 | 4367,3 |
| Number of pensioners, thousand people | 143,9 | 146,0 | 35,1 | 35,3 |
| Total area of residential premises per average city resident (at the end of the year), m2 | 22,2 | 22,7 | 23,2 | 24,0 |
| Number of preschool educational institutions | 94 | 95 | 33 | 33 |
| in them: | ||||
| children, thousand people | 18,0 | 18,6 | 3,6 | 4,0 |
| places, thousand | 12,6 | 12,7 | 3,1 | 3,1 |
| Enrollment of children in preschool educational institutions (at the end of the year), as a percentage of the number of children of the corresponding age | 67,5 | 67,0 | 62,7 | 67,4 |
| Number of daytime educational institutions (at the beginning of the school year) | 80 | 78 | 26 | 26 |
| Number of students in daytime general education institutions, thousand people | 44,2 | 43,7 | 9,7 | 9,4 |
| Number of doctors, people: | ||||
| Total | 3184 | 3287 | 438 | 456 |
| per 10,000 population | 63 | 65 | 39,0 | 41,0 |
| Number of nursing staff, people: | ||||
| Total | 7492 | 7624 | 1797 | 1818 |
| per 10,000 population | 149 | 152 | 160 | 163,5 |
| Number of hospitals | 26 | 26 | 8 | 8 |
| Number of hospital beds: | ||||
| total, thousand | 6,7 | 6,4 | 1,6 | 1,6 |
| per 10,000 population | 132 | 128 | 140 | 140 |
| Number of medical outpatient clinics | 47 | 47 | 11 | 11 |
| Capacity of medical outpatient clinics, visits per shift: | ||||
| total, thousand | 21,9 | 22,3 | 3,5 | 3,3 |
| per 10,000 population | 435 | 444 | 306 | 293 |
| Number of registered crimes | 9906 | 10190 | 1453 | 1394 |
| Persons who committed crimes were identified, people | 2419 | 2244 | 588 | 558 |
| ENTERPRISES AND ORGANIZATIONS | ||||
| Number of enterprises and organizations (at the end of the year; according to state registration) | 13844 | 13520 | 1316 | 1376 |
| MINERAL MINING, MANUFACTURING, PRODUCTION AND DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRICITY, GAS AND WATER1) | ||||
| Number of operating organizations by type of activity (at the end of the year): | ||||
| mining | 6 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| manufacturing industries | 297 | 287 | 134 | 130 |
| production and distribution of electricity, gas and water | 110 | 121 | 25 | 23 |
| Volume of shipped goods of own production, performed works and services by own forces by type of activity, million rubles: | ||||
| mining | 1387,0 | 1718,8 | 242,4 | 338,7 |
| manufacturing industries | 202246,0 | 255365,8 | 5164,5 | 6080,9 |
| production and distribution of electricity, gas and water | 10931,3 | 13304,2 | 936,5 | 1476,2 |
| CONSTRUCTION | ||||
| Volume of work performed for the type of activity “Construction”1) (in actual prices), million rubles. | 8145,2 | 12437,4 | 705,3 | 755,3 |
| Commissioning of social and cultural facilities using all sources of funding: | ||||
| residential buildings, thousand m2 of total area | 343,4 | 384,5 | 63,7 | 64,6 |
| apartments (including apartments in dormitories) | 3597 | 4036 | 604 | 459 |
| preschool institutions, places | 183 | 448 | — | — |
| educational institutions, student places | 748 | — | — | — |
| hospital facilities, beds | — | 160 | — | — |
| outpatient clinics, visits per shift | 100 | 150 | — | — |
| PASSENGER TRANSPORT | ||||
| Number of routes: | ||||
| buses (in intracity traffic) | 46 | 42 | 15 | 15 |
| trams | 5 | 5 | — | — |
| trolleybuses | 9 | 9 | — | — |
| Number of passengers transported per year, million people: | ||||
| by bus (in intracity traffic) | 66,7 | 66,4 | 12,6 | 10,9 |
| by trams | 19,6 | 19,0 | — | — |
| trolleybuses | 32,1 | 30,9 | — | — |
| TRADE1) | ||||
| Retail trade turnover (in actual prices), million rubles. | 20513,6 | 30738,8 | 277,3 | 1165,4 |
| Index of physical volume of retail trade turnover, as a percentage of the previous year | … | 129,3 | … | 362,8 |
| Public catering turnover (in actual prices), million rubles. | 481,1 | 573,6 | 39,1 | 51,1 |
| Index of physical volume of public catering turnover, as a percentage of the previous year | … | 94,2 | … | 103,3 |
| INVESTMENT1) | ||||
| Investments in fixed assets (in actual prices), million rubles. | 24857,0 | 42205,2 | 1752,3 | 1827,5 |
| Share of investments in fixed assets financed from budgetary funds in the total volume of investments, percent | 7,6 | 5,2 | 15,2 | 7,4 |
| including at the expense of the federal budget | 1,2 | 0,9 | 2,9 | 3,3 |
| __________ 1) For organizations not related to small businesses. | ||||
Regions of Russia. Main socio-economic indicators of cities - 2009 Copyright © Federal State Statistics Service
Dankov is a city with developed industry
For little Dankov, they managed to create many enterprises that provide the local population with work.
There are enough municipal buildings here that provide a comfortable life. But, like any small town, Dankov is faced with an outflow of young people. Despite the presence of a fairly large number of enterprises, many do not even want to do an internship here. The same applies to admission to educational institutions. There are simply not enough of them here, so students go to more densely populated cities to get training facilities.
The city authorities of the Lipetsk region demonstrate good work, which has a positive effect on the infrastructure and standard of living of the population. This is what helps ensure that people who go to work in millionaires still return and start families. This is a striking example confirming the possibility of maintaining the required number for the development of regional cities and their centers.
Districts of the Lipetsk region on the map
The entire territory of the region occupies about 25 thousand km2 and is divided into 18 districts. The largest districts in terms of population and area, which can be viewed using maps of the Lipetsk region with diagrams:
- Gryazinsky;
- Lebedyansky;
- Dobrinsky;
- Lipetsky.
The smallest in area, but densely populated district of the region is Khlevensky. It is located in the south of the region on the border with the Voronezh region. The district includes 16 villages, which, if you zoom in on the map of the Lipetsk region with villages, can be examined in more detail.
Railways and highways pass through the main district of the region - Lipetsk, and domestic air flights are also carried out from the airport, which is located in the suburbs. The direction of highways R-119, R-204, R-205, as well as other highways in the region can be viewed using a detailed road map of the Lipetsk region. It will also help you find the main road junctions, bridges, and bypass roads around cities.