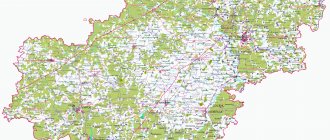
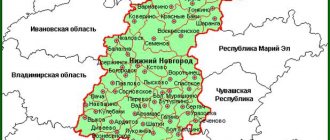
The Leningrad region is located in the north-west of the Russian Federation. The terrain is represented by plains and lowlands, a significant part of which is swampy. If you carefully examine the map of the Leningrad region from a satellite, you will notice that it borders on several constituent entities of the Russian Federation, namely the regions:
- Novgorodskaya;
- Vologda;
- Pskovskaya.
In the north, the borders of the region are limited by Karelia. Also, the Leningrad region has common borders with Estonia and Finland.
The regional government is located in the city of St. Petersburg; it can be viewed on a map of the Leningrad region by district. What is atypical for our country is that it is not part of the region, but is a semi-enclave territory.
Most of the hydrographic objects in the region appeared thanks to the Baltic Sea basin. Therefore, in the north-west of the region there is a huge number of rivers and lakes. The largest rivers that can be found on the map of the Leningrad region with diagrams include:
- Pasha;
- Oyat;
- Meadows;
- Volkhov;
- •Syasya.
If you add up the lengths of all the rivers in the region, you get more than 50 thousand km. One of the most significant hydrographic objects is also Lake Ladoga - the largest in area in Europe and one of the deepest in the country.
If you zoom in on the map, you can take a closer look at the districts on the map of the Leningrad region, the cities that are part of them, as well as the streets and houses.
Districts of the Leningrad region on the map
The region is divided into 17 districts. The largest districts by area:
- Vyborg;
- Tikhvinsky;
- Luzhsky;
- Boksitogorsky;
- Podporozhsky.
The infrastructure, location of streets, roads, houses, administrative buildings, train stations and attractions in each district will be helped by a map of the Leningrad region with settlements.
More than 30 major highways pass through the region, connecting the region with St. Petersburg, the Scandinavian countries, Moscow and other Russian cities. Part of the ring road around St. Petersburg passes through the Lomonosov and Vsevolozhsk districts, which can be seen on the detailed road map of the Leningrad region.
Passenger and cargo transport is also carried out by shipping. There are such large ports in the region as:
- Vysotsk;
- Ust-Luga;
- Primorsk;
- Kronstadt;
- Vyborg.
In addition to sea transport, large river vessels sail along the Neva and Volkhov rivers. Since Soviet times, the western regions of the region have remained a border zone through which ferries with automobile transport, cargo and passenger ships pass. If you look at the map of the Leningrad region in detail, you can find all the port border cities of the region.
To get to other cities in the country and abroad, residents of the region can use the only passenger airport of international importance, Pulkovo, which is located on the outskirts of St. Petersburg.
Vyborg is the largest in the Leningrad region
The largest settlement in the Leningrad region is Vyborg - one of the most interesting tourist destinations and a real island of the Middle Ages among luxurious imperial palaces and quaint noble estates. However, it cannot be called a metropolis - 160,847 km² and 77,400 citizens. The density is relatively low: 481.2 people/km². For example, in Moscow the level is 10 times higher and amounts to 4,931.78 km².
Since ancient times, Vyborg has had important strategic importance, acting as an outpost between the Scandinavian countries and the Russian state, as well as providing access to the sea. The official founding date of the city is 1293, when the Swedes founded the Vyborg Castle. However, it is known that the Korel tribes lived here already at the beginning of the first millennium. Today, the fortress built by Swedish soldiers and the buildings inside the massive stone walls are the main attractions of the city, attracting hundreds of thousands of tourists every year. Fortecia changed hands more than once until it was finally conquered by Peter the Great in the 18th century. However, after the revolution of 1917, the city went to Finland, returning to the USSR only after the Great Patriotic War: dilapidated and deprived of its former grandeur. The population grew rapidly: in the first post-war year alone it increased from 2,500 to 16,414, and by 1996 it reached 81,200. Despite the abundance of historical monuments, 35% of Vyborg’s income comes from industry, represented by such areas as:
- production of building materials;
- shipbuilding;
- food production;
- mechanical engineering;
- production of auto parts.
During many years of restoration work, most of the attractions were restored. The most atmospheric part of Vyborg is the Old Town, which is located behind the fortress walls. Walking along the cobblestone streets along the gloomy stone houses, you feel as if you are entering the medieval past of the castle. Authentic restaurants and themed events, such as knightly tournaments and fairs, add additional flavor. Among the most beautiful buildings in the city is the Vyborg Town Hall from the 17th century. The tallest building is the watchtower of St. Olaf, rising above the castle, and the oldest, made of stone, is the Merchants' Guild House, built in the 14th century.
Map of the Leningrad region with cities and villages
There are more than 30 large cities in the region, all settlements, both large and small, can be seen on the map of the Leningrad region with cities and villages. The most significant settlements in the region in terms of area and number of people living are:
- Vyborg;
- Tikhvin;
- Gatchina;
- Sertolovo;
- Pinery;
- Volkhov;
- Kingisepp.
Almost all cities have characteristic “northern” architecture and many historical monuments. Architecture and identity of the local population. Thousands of tourists arrive in the region every day who want to see the most beautiful architectural and historical monuments in Russia, which are indicated on the map of the Leningrad region with villages. The main attractions and most interesting places in the region:
- Ulyanovka village – Sablinskie caves;
- Belogorka village – Eliseev’s estate;
- Nevsky Parkleskhoz village - the ancient Church of the Intercession;
- Priozersk – Konevets Island;
- Vyborg - Mon Repos;
- The city of Gatchina is a museum-reserve.
The list of attractions can be endless. If you go to visit this historical region of the country, use Yandex maps of the Leningrad region, which will become an indispensable assistant on your trip.
Volkhov is large in area, but its numbers are decreasing
Volkhov ranks only ninth in population with a population of 44,868, but in size it ranks second in the ranking with an indicator of 108.21 km². This is largely due to the fact that it was formed by the merger of several settlements:
- Zvanki station;
- workers' settlement Volkhovstroy for hydroelectric power plant builders;
- workers' village of Proletarsky;
- 5 small villages and hamlets.
In addition, Volkhov stands on two banks of the river of the same name, forming areas quite distant from each other. There are very few manufacturing enterprises in Volkhov: not counting hydroelectric power stations, there are only 8 of them, most of which are involved in the food industry. There are two branches of St. Petersburg universities, as well as several local colleges. Due to a lack of promising vacancies and a small variety of educational institutions, the last two decades have seen a decline in the number of city residents. Over the last decade, their number has decreased by more than 5,000 due to the migration of young people to Moscow and St. Petersburg, as well as a reduction in natural increase.
Economy and industry of the Leningrad region
The region's economy is represented by many industries. Hunting, fishing and forestry have always been and remain traditional for the region. The leading positions are occupied by such sectors of the economic sphere as:
- transport and communications;
- manufacturing;
- construction;
- energy.
A large number of enterprises in the light, food and processing industries operate in the region. Here they sew shoes, clothes, and produce plastic and metal products.
A great contribution to the region’s economy comes from investors who see great opportunities in the region for developing large businesses and opening large-scale investment projects.
Kirovsk is large in size, but not in number of inhabitants
Large in size (84.9 km²) and small in population (26,387 people) is Kirovsk, founded in 1931 and named after the revolutionary Kirov. There are plenty of jobs here: there is a state district power station and 10 industrial enterprises. In this regard, since 2000, the number of city residents, although slowly and unstable, has been growing: the value has increased by 3,000 over 20 years.
There are few attractions in Kirovsk, most of them are related to the Great Patriotic War. The most significant is the open-air museum “Breakthrough the Siege of Leningrad,” since bloody battles for the fate of the besieged city took place in the surrounding area. Among the unusual monuments is the sculpture of Peter I, recreated in 2013 according to surviving drawings, which was created by Putilov stonemasons in the mid-19th century on the outskirts of modern Kirovsk.
Total population
The history of observations of the number of inhabitants in Russia begins during the Tatar-Mongol invasion. However, separate information on various subjects, including the Leningrad region, appeared only in Soviet times. Due to the fact that the region changed its borders several times during the years of Soviet power, there is no definitively reliable figure on the number of residents. Today, the total population of the Leningrad region is 1,778,890 people (according to statistics for 2021).
Sosnovy Bor is a closed city with interesting monuments
Sosnovy Bor is the only city on the list that is simultaneously in fourth place in terms of number of inhabitants and size with values of 68,045 people and 72 km². Despite the fact that it was given city status only in 1958, the small village of Ustya was listed on the Ingrian map of 1676. The town is famous primarily for the nuclear power plant located here. In 1981, it was considered the largest in the world, and in 2002 it set a European productivity record, producing the 600th billion kWh. Because of the nuclear power plant, it is one of the so-called closed cities: foreigners are prohibited from entering here without special permission, and since 2013 Russians are allowed only with a passport.
In this regard, the town has themed attractions. Among them are a bust and a monument to Anatoly Petrovich Alexandrov, one of the founders of nuclear energy in the USSR, as well as a monument to the liquidators of the consequences of the nuclear power plant accident in Chernobyl. However, another one is more famous - Andersengrad: a children's entertainment area, stylized as a medieval town, as if straight from the pages of Andersen's fairy tales. It attracts not only kids: against the backdrop of cobblestone walls and houses with tiled roofs, atmospheric photographs are obtained.
Demographics
Fertility is the most important demographic indicator that demonstrates the degree of well-being of a region. Social protection of the population of the Leningrad region is a pressing issue. The relevant committee notes that since 2011, the birth rate in their territory has been growing, albeit at a very slow pace, by about 2 people per 1000 inhabitants. But, according to sociologists, the birth rate will decline slightly in the coming years.
The second most important indicator is mortality. For several years in a row in the 21st century, a decrease in mortality was observed in the Leningrad region. But since 2014, the number of deaths began to increase again, and it is expected that this trend will continue in the next 5 years. Thus, in the Leningrad region there is a natural population decline, by approximately 5 people for every thousand inhabitants. Migration growth has been increasing in recent years; sociologists note that quite a lot of women of childbearing age are coming, this allows us to hope that the situation with the birth rate will soon improve. The largest sources of migrants are Ukraine, Belarus, Kyrgyzstan, and Moldova. Sociologists predict a slight decrease in the number of arrivals due to problems in the labor market.
Life expectancy is the third most important criterion for the well-being of a region. How are things going with him in the subject of the Russian Federation we are considering? The average life expectancy in the Leningrad region is 70.2 years: women live approximately 75 years, men - 64 years.
All these data allow us to say that the Leningrad region, whose population is gradually aging, fits into the general trends of Russia. The region cannot yet move to a productive, youthful type, and there are many socio-economic reasons for this.
Content
- 1 Medium-sized cities 20-100 thousand people 1.1 Gatchina
- 1.2 Vyborg
- 1.3 Vsevolozhsk
- 1.4 Sosnovy Bor
- 1.5 Tikhvin
- 1.6 Kirishi
- 1.7 Sertolovo
- 1.8 Kingisepp
- 1.9 Volkhov
- 1.10 Tosno
- 1.11 Meadows
- 1.12 Shales
- 1.13 Kirovsk
- 1.14 Otradnoe
- 1.15 Communard
- 1.16 Nikolskoye
- 1.17 Pikalevo
- 2.1 Lodeynoye Pole