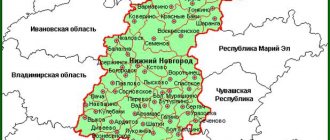
If we consider the Central Federal District, then in its southwestern part you can see a small area dissected by a large number of rivers. This is the Kaluga region. According to scientists, settlements existed on this land for several thousand years BC. On the satellite map of the Kaluga region, borders with several regions are visible:
- Tula;
- Bryansk;
- Orlovskaya;
- Moscow;
- Smolenskaya.
The regional center of the region is the city of Kaluga, located only 140 km from the Moscow Ring Road. The region has a developed infrastructure, the objects of which can be studied using a map of the Kaluga region by district. This convenient online service allows you to find any cities and towns, examine their structure, main and small streets, houses, administrative and natural objects.
The entire water system of the region belongs to the Oka basin. More than 2,000 rivers, rivulets and streams flow through the region. About 300 of them are longer than 10 km.
The main rivers that can be found on the map of the Kaluga region with diagrams:
- Protva;
- Ugra;
- Bolva;
- Ressa;
- Zhizdra;
- Oka.
There are about 500 peat bogs on the territory of the Kaluga region. The largest number of them is located in the western and northwestern parts of the region, through which the Ugra River and its tributaries flow.
Natural conditions
The satellite map of the region clearly shows how the central watershed of the Russian Plain passes through its territory.
It separates the Dnieper and Volga basins. In total, more than 2,000 rivers flow through the region. Forests are rightfully considered the main natural wealth of the Kaluga region. They cover more than 45% of the entire territory. Conventionally, they can be divided into 2 types: broad-leaved and coniferous. Thanks to the diverse flora, there are 4 ecological settlements in the region: a nature reserve, a wildlife sanctuary, a large national park and the Kaluga Forest natural monument.
Physiographic location of the Kaluga region
The Kaluga region is located in the ]East European[/anchor] plain, approximately at an equal distance (800-850 km) from the White, Baltic, Azov and Black Seas. Its territory is 29.9 thousand km2. This is one of the smallest regions in the European part of the country.
In the west, the Kaluga region borders with Smolensk, in the south with Bryansk and Orel, in the east with Tula, and in the north with Moscow regions. In area it is inferior to the Bryansk, Smolensk and Moscow regions. However, the Kaluga region is larger in size than six dozen countries in the world, including Albania, Macedonia, Equatorial Guinea, El Salvador, Jamaica, and Fiji.
From north to south, the region's territory stretches for more than 220 km. The northernmost point is located 6.9 km north of the village of Mityaevo (55°20'32″ N), the southernmost point is 5.2 km southwest of the village of Kossy (53″16″ 42″ N). From west to east, the territory of the Kaluga region stretches for more than 240 km. The extreme western point is located 2.8 km southwest of the village of Linevka (33°26'40″ E), the extreme eastern point is 1.6 km east of the village of Guryevo (37°16'40 ″E.D.). In general, the region extends from northeast to southwest.
The very size itself determines the internal geography of the region, allowing us to talk about a certain diversity of its nature, population and economy.
The location of the region in the middle latitudes determines the moderate amount of solar radiation entering its territory, the clear predominance of moderate air masses throughout the year, as well as the nature of their circulation. Despite the relatively large distance from the seas of the Atlantic Ocean (about 800 km), the climate of the territory experiences its softening effect.
The Kaluga region is located within the ancient Russian (East European) platform. This was reflected in its relief, tectonic structure and features of geological deposits. The territory of the region was repeatedly covered by ancient glaciers, which had a significant impact on the formation of modern relief.
The territory of the Kaluga region is located within two water basins. Most of it belongs to the Volga basin (Caspian Sea), and the smaller part belongs to the Dnieper basin (Black Sea). The largest rivers in the region are the Oka, Ufa, Zhizdra, Protva, Bolva, etc.
The location of the region on the border of forest and forest-steppe zones determines the diversity of soil, vegetation and animal life. Unique natural landscapes are included in the system of specially protected natural areas, the most significant of which are the Ufa National Park and the Kaluzhskie Zaseki Nature Reserve.
Transport connections of the Kaluga region, roads and routes
Road and railway transport are well developed in the Kaluga region. Thus, on the online map with the borders of neighboring regions, the main highway “Ukraine”, which passes through Balabanovo, clearly stands out. Also, a federal highway Moscow – Warsaw is laid across the region.
There are several roads of regional importance in the region with fairly high traffic intensity. In 2014, 2 important roads were put into operation: Golodskoye – Suvorov – Odoev and Meshchovsk-Kudrinskaya. The first route runs directly to the borders of the Tula region, the second goes to the Moscow-Bryansk railway.
An important railway junction in the region is the Moscow-Kyiv highway, which passes through Balabanov and Obninsk. In addition, 6 diesel locomotive lines and the Bryansk - Dudorovsky branch were developed.
Speaking about transport, one cannot fail to mention the Kaluga international airport, built near the regional center of the same name.
Content
- 1 Large cities 250 - 500 thousand people 1.1 Kaluga
- 2.1 Obninsk
- 3.1 Lyudinovo
- 4.1 Kozelsk
Kaluga region with districts and cities on the map
On the map of the Kaluga region there are 24 districts and 2 cities of regional significance. In addition, there are 252 rural settlements and 26 urban settlements in the region. According to the census, as of July 31, 2021, the total population of the region slightly exceeded 1 million people, while most settlements are experiencing a decline in the birth rate and population decline.
The largest and main city in the region is Kaluga. The total population is about 342 thousand people. The city has 3 railway stations that connect the region with Moscow, Tula, Smolensk and Ukraine.
The second large city, with a population of about 114 thousand people, is Obninsk. Located at the intersection of the Moscow-Kyiv and Moscow-Brest highways, just 80 km. from MKAD.
Kaluga region
Kaluga region is a subject of the Russian Federation. Belongs to the Central Federal District. The administrative center is the city of Kaluga. The region borders on Moscow, Moscow, Tula, Bryansk, Smolensk, and Oryol regions. The region is located in the central part of the East European Plain. The area is 29,777 sq km, the population, as of 2021, is 1 million people. The climate is temperate continental with distinct seasons.
Initially, Kaluga was a fortress that protected Moscow from attacks from enemies from the south and west, but gradually, due to the expansion of the state’s borders, this status lost its relevance. In the center of the city, many monuments of civil architecture of the 18th-19th centuries have been preserved, including public places, Gostiny Dvor, Khlyustinsky charitable institutions, Korobkov chambers, Berezuevsky Bridge. Here is located the world's first and largest space museum in Russia - the State Museum of the History of Cosmonautics named after K.E. Tsiolkovsky. The heart of Kaluga's historical past is the City Park of Culture and Leisure.
The region is rich in architectural and natural attractions. Mentions of the first large cities of the region date back to the 12th century. The ancient history is evidenced by many monuments of temple and civil architecture of different eras and styles. The area is created for cultural tourism and recreation, it will delight any travel lover. The Kaluga region is famous for its ancient monasteries, among which the Tikhonova and Optina Monasteries, the Pafnutev Borovsky and Nikolaevsky Chernoostrovsky monasteries stand out. The Kaluga region is an ideal place for hunting and fishing. There are many rivers and forests here. Lovers of a quiet holiday in nature are attracted by the state-protected territories of the region, natural monuments of regional and all-Russian significance. Among them is the Rezvan mineral spring.
The region has all the conditions for eco-tourism. One of the attractions of the Kaluga region is the ethnographic park-museum “Ethnomir”, in the Borovsky district. On its territory of 140 hectares there are thematic corners illustrating the architecture, culture and traditions of different peoples of the planet. In addition to numerous excursions, master classes and games organized near each ethnic yard, visitors to the park-museum can enjoy sports grounds, a climbing wall, a rope course, ATVs, Segways, golf carts, husky riding and much more. In addition to weekend and weekday programs, Ethnomir hosts various festivals and national holidays.
see also
- Kaluga region
- Cities of Russia
| [ + ] Cities by regions of Russia | |
| Cities of the North-West (NWFD) | St. Petersburg (and its cities) • Leningrad region (historical Staraya Ladoga) • Arkhangelsk region • Vologda region • Kaliningrad region • Karelia • Komi • Murmansk region • Nenets Autonomous Okrug • Pskov region |
| Cities of the Volga region (Volga Federal District) | Bashkortostan • Volgograd region • Kalmykia • Kirov region • Mari El • Mordovia • Nizhny Novgorod region • Orenburg region • Penza region • Perm region • Samara region • Saratov region • Tatarstan • Udmurtia • Ulyanovsk region • Chuvashia |
| Cities of Southern Russia (SFD) | Sevastopol (including Inkerman) • Republic of Crimea • Adygea • Astrakhan region • Krasnodar region • Rostov region |
| Cities of the North Caucasus (NCFD) | Dagestan • Ingushetia • Kabardino-Balkaria • Karachay-Cherkessia • North Ossetia - Alania • Stavropol Territory • Chechen Republic |
| Cities of the Urals (Ural Federal District) | Kurgan region • Sverdlovsk region • Tyumen region • Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug - Yugra • Chelyabinsk region • Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug |
| Cities of Siberia (Siberian Federal District) | Altai Republic • Altai Territory • Irkutsk Region • Kemerovo Region • Krasnoyarsk Region • Novgorod Region • Novosibirsk Region • Omsk Region • Tomsk Region • Tyva • Khakassia |
| Cities of the Far East (FEFD) | Amur Region • Buryatia • Jewish Autonomous Region • Trans-Baikal Territory • Kamchatka Territory • Magadan Region • Primorsky Territory • Sakha (Yakutia) • Sakhalin Region • Khabarovsk Territory • Chukotka Autonomous Region |
| see also | Cities of the DPR, LPR, Transnistria, South Ossetia • Regions of Russia • Cities of Russia |
Small towns up to 20 thousand people
Kozelsk
Population 16,045 people (2016).
Kondrovo
Population 15,146 people (2016).
Sukhinichi
Population 15,144 people (2016).
Zhukov
There are other meanings of this name
Population 12,844 people (2016).
Borovsk
Population 11,210 people (2016).
Sosensky
Population 11,008 people (2016).
Kremenki
Population 10,774 people (2016).
Ermolino
Population 10,263 people (2016).
Tarusa
Population 9,267 people (2016).
Belousovo
Population 8,914 people (2016).
Medyn
Population 7,849 people (2016).
Yukhnov
Population 6,153 people (2016).
Zhizdra
Population 5,506 people (2016).
Spas-Demensk
Population 4,342 people (2016).
Mosalsk
Population 4,084 people (2016).
Meshchovsk
Population 4,036 people (2016).