To understand the territorial organization of the Russian Federation, the concept of administrative-territorial division is used. On its basis, the work of government structures at all levels (federal, regional, local) is organized. This unusual type of administrative-territorial division is due to the large area of the state. The reason is also a combination of various factors that influence each subject of Russia - geographical, national, natural, and so on.
Geography
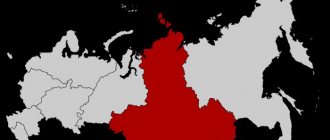
The area of the Central Federal District is 650,205 km2, which is 3.8% of the entire area of Russia. If we compare this district with European countries, it is larger than Ukraine, which is considered the largest among the western neighbors of the Russian Federation. Located entirely on the East European Plain. Includes such hills as Valdai, Central Russian, Smolensk-Moscow. There are also lowlands: Oksko-Donskaya, Meshcherskaya.
Rice.
1. Central Federal District The highest point is considered to be the top of Valdai, which is 347 meters above sea level.
In the west, the Central Federal District borders on Belarus, in the southwest - on Ukraine. This applies to external borders. If we consider the internal border territories, then the southern part borders on the Southern Federal District, in the eastern part - on the Volga District, on the northern side - on the Northwestern Federal District. The number of people living here at the beginning of 2021 is 39,318.0 thousand people, which is 26.77% of the total population of the country. With a density of 60.5 people. km2. The largest rivers in Russia - the Volga, Oka, Don, Western Dvina - flow through the territory of the Central Federal District. There are such natural areas as:
- Mixed forests
- Forests with broadleaf trees
- Steppe zones
- Forest-steppe territories
Rice. 2. Red Square
Inland waters
The reservoirs of Central Russia play a huge role in the formation of unique relief and natural features. In addition, settlements were formed around large rivers and lakes from ancient times, which have now grown into large cities - Moscow, Voronezh, Yaroslavl, Kursk, Orel, Tula, Lipetsk, Kaluga, Vladimir, Ivanovo.
Deep rivers flow through Central Russia, which are important not only for Russia, but also for neighboring countries. On the territory of the districts there are basins of the Volga (the largest tributary of the Oka), the Dnieper (a tributary is the Desna River), the Don (2 tributaries - the Khoper River and the Northern Donets River) and the Western Dvina. Another important tributary of the Oka is the Moksha River.
The following rivers are considered navigable: Volga, Oka, Moscow, Don, Dnieper, Sura, Vyatka and Vetluga. Many of them have access to the seas (Baltic, Caspian and Black). With the growth of cities and settlements in the Central regions, there is a shortage of water. Therefore, it is so important to create and properly operate both artificial and natural reservoirs.
The largest artificial reservoir is Rybinsk in the Yaroslavl region. Its area is 4580 km² and its water volume is 25.4 km³. They began to build it on the bed of the Volga River in 1935, for this purpose they resettled and flooded 663 settlements. But it was completely filled only in 1947.
Now the Rybinsk Reservoir has important economic and natural significance: energy production (Rybinsk State Power Plant with a capacity of 356 MW), fishing and shipping, as well as protected areas (Darwin Nature Reserve).
Along with Rybinsk, the district has several other large reservoirs:
- Verkhnevolzhskoye in Tverskots region.
- Ivankovskoye in the Moscow region.
- Uglichskoe in the Yaroslavl region.
- Yauzskoe in the Smolensk region.
The district is rich in lakes. The largest include Seliger (Tver and Novgorod regions), Lake Galichskoye (Kostroma region), lakes Nero and Pleshcheyevo (Yaroslavl region) and Lake Volgo (Tver region).
In the north of the district there are numerous swamps and wetlands. The largest in area are in the Tver region. These are the well-known Upper Volga swamp complex and the Zharkovsko-Svitskie swamps, as well as the Orsha moss. The total area of marshes and wetlands in the county is more than 12,000 km².
Another amazing creation of man is an artificial canal that connects 2 rivers - the Volga and Moscow. The canal has a length of 128 km, runs through the Tver region, along the Moscow region and partially covers the capital. The canal supplies Moscow with 60% industrial and drinking water.
Natural resources
This federal district has the most iron ore minerals. Their main deposits are located in the Kursk magnetic anomaly. According to statistics, this anomaly ranks first in the world ranking in terms of geological reserves.
However, iron ore is not the only thing the Central Federal District is rich in. Large deposits of such resources as:
- Chalk
- Limestone
- Fireproof clay
- Marl
- Glass and molding sand
If we consider the resources intended for use as fuel (fuel and energy complex), then most of them are expressed in the form of brown coal in the Moscow region. It even spreads in areas such as:
- Tverskaya
- Kaluzhskaya
- Ryazan
- Smolenskaya
There are peat deposits in the Kostroma and Yaroslavl regions.
Rice. 3. Yaroslavl tire plant
Composition of federal districts
Periodically, the composition of the Federal District was changed in order to more conveniently control the implementation of various activities to solve federal problems. The last change was carried out in 2021. At the moment they are not planned. At the moment things are as follows:
- Central Federal District - 17 regions (Belgorod, Bryansk, Vladimir, Voronezh, Ivanovo, Kaluga, Kostroma, Kursk, Lipetsk, Moscow, Orel, Ryazan, Smolensk, Tambov, Tver, Tula, Yaroslavl) and one city of federal significance - Moscow.
- Northwestern Federal District - 7 regions (Arkhangelsk, Vologda, Kaliningrad, Leningrad, Murmansk, Novgorod and Pskov), one federal city - St. Petersburg, one republic - Komi, as well as the Nenets Autonomous Okrug.
- Volga Federal District - 8 regions (Nizhny Novgorod, Kirov, Ulyanovsk, Penza, Saratov, Samara and Orenburg) and 6 republics - Tatarstan, Mari El, Chuvashia, Udmurtia, Bashkortostan, Mordovia, as well as the Perm Territory.
- Southern Federal District - 3 regions (Astrakhan, Volgograd and Rostov), 3 republics - Kalmykia, Adygea and Crimea, one federal city - Sevastopol, Krasnodar Territory.
- North Caucasian Federal District - 6 republics (Karachay-Cherkessia, Kabardino-Balkaria, North Ossetia-Alania, Ingushetia, Chechnya and Dagestan), Stavropol Territory.
- Ural Federal District - 4 regions (Tyumen, Chelyabinsk, Kurgan and Sverdlovsk) and three autonomous districts - Yamalo-Nenets, Khanty-Mansiysk and Ugra.
- Siberian Federal District - 5 regions (Irkutsk, Kemerovo, Novosibirsk, Omsk and Tomsk), 3 republics - Altai, Khakassia, Tyva and two territories - Altai and Krasnoyarsk.
- Far Eastern Federal District - 3 regions (Amur, Magadan and Sakhalin), 2 republics (Buryatia and Yakutia), Transbaikal and Kamchatka territories, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug and Jewish Autonomous Region.
Agro-industrial complex (AIC)
More than 33 thousand hectares are provided for agriculture in the Central Federal District. Thanks to the fertile soils, most of which are podzolic and sod-podzolic, crops such as:
- Wheat
- Rye
- Oats
- Barley
- Buckwheat
The livestock sector of the agro-industrial complex is no less well developed. In particular, these are meat and dairy animals, pig farming, poultry farms, and sheep farms. Honey production and fish farming occupy a special position.
Rice. 4. Main building of Voronezh State University
Transport network
The Central Federal District is one of the districts in which there are absolutely all types of transport routes: railway, road, underground, aviation, water and others. In total, the structure of the transport network is as follows:
- 70 main railway junctions
. The most important among them and throughout Russia is the Moscow Transport Hub (MTU). - 28 airports of various aviation types
. This does not take into account especially large ones, such as Sheremetyevo, because they are located in the zone of direct influence of Moscow. - More than 17,000 km of railway lines
. - The total length of
paved highways is more than 227,000 kilometers. - The length of waterways
within the district is 5.5 thousand km. Although the district does not have direct access to the waters of the seas and oceans, thanks to several river networks, ships from the Central Federal District can go to both the Baltic and the Caspian, White, Azov, and Black Seas.
The Central Federal District has international transport routes, such as the Trans-Siberian Railway, which goes straight to Vladivostok.
Important! The Central Federal District also has several oil pipelines, oil product pipelines, and a main gas pipeline.
Centers of federal districts
As already mentioned, all federal districts have city centers, within which certain authorities are located that control the activities of the entire district. They do not always coincide with the largest populated area of the administrative-territorial unit. All information can be seen in the table.
| Name of the federal district | Center |
| Central Federal District | Federal city – Moscow |
| Northwestern Federal District | Federal city – St. Petersburg |
| Volga Federal District | Nizhny Novgorod |
| Southern Federal District | Rostov-on-Don |
| North Caucasian Federal District | Pyatigorsk |
| Ural Federal District | Ekaterinburg |
| Siberian Federal District | Novosibirsk |
| Far Eastern Federal District | Vladivostok |
A change in center is possible only if a certain entity moves from the department of one territorial-administrative unit of a new type to another. Of the above settlements, Pyatigorsk and Nizhny Novgorod are not the largest in their federal districts.
Market infrastructure
The development of the market system in the Central Federal District is 5 steps ahead of all other districts and regions. In this regard, it accounts for 14.6% of all-Russian indicators. In the Central Federal District, according to the latest statistics from Russian analysts, there is a high rate of development, reaching 25%. As for taxes that are paid directly to the federal budget, then the mark crosses the threshold of 45%.
Rice. 5. Moscow Refinery
Map of federal districts
For convenient familiarization with the territory occupied by the federal districts, appropriate geographical maps have been developed. You can find them in special atlases or on online resources. Among the latter, a good option is the site https://geostudy.ru/fo.html.
The convenience of maps lies in the fact that in addition to boundaries and occupied area, you can see the location of cities and other settlements, as well as geographical features - the location of reservoirs, forests, mountains, agricultural land, and so on.
Industry
All industries are highly developed in the Central Federal District. Based on this, the following statistics were made, reflecting the general indicators and level of academic performance in relation to other constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Let's look at specific data using the example of the Moscow region:
- Metal processing accounts for almost 39% of all-Russian indicators
- Electric power industry - 11%
- Construction production - 11.3%
- Food industry - 9.1%
- Light industry - 10%
- Khimprom - almost 8%
- The woodworking industry accounts for - 5%
- Non-ferrous metallurgy about 3.5%
- Ferrous metallurgy - 2.3%
Mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering occupies a major position in the Central Federal District. Recently, the machine tool industry, aircraft manufacturing, electrical power equipment, electrical appliances and carriage building have become particularly widespread. The main center of this field of activity is the capital of the Russian Federation - Moscow. The main ZIL enterprise, which produces trucks, is located here. There are numerous enterprises producing machine tools for all types of industries: food, textile, woodworking and others.
Population
Of the total population of almost 39 million people, there are many different nationalities in the Central Federal District - there are about 28 of them. Let's look at the nations that make up the bulk:
- Russians make up the bulk of the population - 89.10%
- Representatives of Ukraine - 1.34%
- Armenian citizens - 0.71%
- Tatars - 0.69%
Due to such a wide national composition, there are 9 language groups, which are united into 7 families:
- Indo-European family consisting of Slavs, Armenians, Iranians, Romanians, Indo-European Jews and Indo-Aryans. The main part, naturally, is occupied by representatives of the Slavic family - more than 90%.
- The Altai family includes the Turks and Mongols.
- Ural family consisting of a Finno-Ugric group.
- North Caucasian family.
- Kartvelian family.
- Korean family.
- Semitic-Hamitic family.