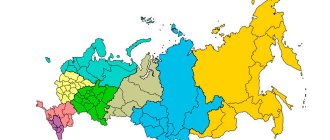
The Siberian Federal District (SFO) is an administrative formation in Russia, formed on May 13, 2000 by decree of the President of the Russian Federation. Its population is 19.25 million (2010 census). Finding the Siberian Federal District on the map is not difficult, because it occupies 30 percent of the territory of our country. Up to 85 percent of all-Russian reserves of platinum and lead, 80% of molybdenum and coal, 71% of nickel, 69% of copper, 44% of silver, 40% of gold are concentrated here. In the total volume of industrial production, the share of the Siberian Federal District in 2013 was 11.2 percent.
Siberian Federal District: composition
The formation includes twelve subjects of the federation, including five regions (Omsk, Novosibirsk, Irkutsk, Tomsk, Kemerovo), four republics (Khakassia, Buryatia, Altai, Tyva) and three territories (Trans-Baikal, Altai, Krasnoyarsk). The capital of the Siberian Federal District (administrative center) is the city of Novosibirsk. In total, there are 4,114 municipalities in the Siberian Federal District, of which 319 are municipal districts, 257 urban settlements, 77 urban districts, and 3,461 rural settlements. Settlements with a population of more than one hundred thousand people are Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, Irkutsk, Novokuznetsk, Omsk, Tomsk, Kemerovo, Bratsk, Barnaul, Seversk, Ulan-Ude, Biysk, Norilsk, Angarsk, Berdsk, Kyzyl, Prokopyevsk, Chita, Rubtsovsk, Achinsk, Abakan.
Civil War
It was Novosibirsk, in 1917 Novo-Nikolaevsk, that was destined to become the city where the Civil War began, since historians consider it to be the beginning of the uprising of the Czechoslovak Legion. A Czech unit located in the city, together with the officer underground, overthrows Soviet power in the city. At the same time, the Siberian Autonomous Region was formed in Tomsk and a provisional Siberian government was formed. But already in November 1919, units of the Fifth Red Army liberated the Siberian regions, in which Soviet power was established.
Territory
The Siberian Federal District has a total area of 5114.8 thousand square kilometers, the length of the territory from west to east is 3420 kilometers, from north to south - 3566 kilometers. In the west, the Siberian Federal District borders on the Yamalo-Nenets and Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrugs, the Tyumen Region; in the north - only with the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug; in the south - with Mongolia, Kazakhstan and China; in the east - with the Amur region and the Republic of Yakutia (Sakha). The length of the state border is 7269.6 kilometers, including with Kazakhstan - 2697.9 kilometers, with China - 1255.5 kilometers, with Mongolia - 3316.2 kilometers. The Siberian Federal District includes 108 border outposts, 68 customs posts and border checkpoints.
Infrastructure of Kemerovo
Is it worth moving to the city for permanent residence? The question is ambiguous, but it is worth noting that living here is comfortable. The problems of bad roads are gradually being solved, and highways within the city can boast of almost exemplary smoothness. But the roads are narrow, and there is a lot of traffic, so transport hubs are overloaded. That’s why the courtyards are always filled with cars, especially Lenin Avenue and Tereshkova Street. In addition, a federal highway with a flow of trucks passes through the city. But the city is far from overcrowded and this seriously smoothes out the situation. In 2014, the wide Kuznetsky Bridge was built.
The city has public transport, namely trams, trolleybuses, taxi and bus routes. The fare is steadily rising. You can get out of the city by rail, highways or by road. Buses run throughout the region and even to neighboring countries. The city's airport is a hub for international transportation, but it will be cheaper to book tickets from Novosibirsk.
Housing and communal services issues are the most important for the entire country, and in Kemerovo the situation is not significantly different from other cities. Almost all citizens install separate meters.
Even in the last century, the city was almost entirely made up of wooden houses, barracks on one floor. High-rise buildings began to be built only in the sixties, and the Central District was the first to be built. By the way, development is actively underway now, so there are no problems with real estate. The size of the city is very non-standard and the ratio of multi-storey and private houses is approximately equal. In general, the picture is quite pleasant, since the city has a developed center.
The city's social policy is very active, queues for kindergartens drag on for years, but there are no problems with enrollment in schools. In addition, innovative projects are being implemented across the region on scientific platforms; You can choose schools for your child according to his abilities and wishes. Further, parents have a choice of 7 state universities, 5 branches and 2 non-state educational institutions.
Population
The share of the total population of Russia is 13.48 percent. Density: 3.7 people per square kilometer. This formation is characterized by a significant preponderance of the urban population over the rural: 72 percent versus 28. Residents of the Siberian Federal District are predominantly Russian (87.38 percent). The population of the Siberian Federal District is also represented by Buryats (2.13%), Ukrainians (1.86%), Germans (1.54%), Tatars (1.26%), and Tuvans (1.2%). Less than one percent of the total population are Kazakhs, Khakassians, Belarusians and Altaians.
Ecological situation
Until 2011, Omsk was considered one of the most polluted cities in the country. However, in recent years the environmental situation has improved. The reason for the improvement was the modernization and slowdown of city enterprises. However, the problem of transport pollution persists. The problem of landfills, which affect river pollution, also remains relevant. The waters of large rivers remain in an unsatisfactory ecological condition.
Economy
The leading sector of formation is industry; in 2012 it accounted for 37.2 percent of gross value added (in the Russian Federation on average - 32.3 percent). The gross regional product in 2012 amounted to 5147.4 billion rubles (10.3 percent). GRP per capita – 267.1 thousand rubles (in the Russian Federation – 348.6 thousand rubles). In the total volume of shipped industrial products in Russia, the share of the Siberian Federal District in 2013 was 11.2 percent. Products produced per capita amounted to 234.4 thousand rubles (in the Russian Federation - 280 thousand rubles). In the total volume of Russian agricultural production, the share of formation in 2013 was 13.6 percent. Agricultural products worth 515.3 billion rubles were produced, per capita – 71.5 thousand rubles (in the Russian Federation – 92.5 thousand rubles). With all this, the volume of foreign investment in the Siberian Federal District is insignificant - only 412 US dollars per capita, while in the Russian Federation - 1187 US dollars. Foreign trade turnover, according to customs statistics, in 2013 amounted to 45.5 billion US dollars, of which 36.2 billion were exports and 9.2 billion were imports.
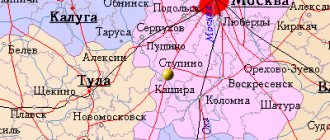
Geography and climate of Kemerovo
So, the city itself is almost 3 thousand kilometers in a straight line from the capital. On roads this distance increases to 3601 km. The two parts of the city are located on the banks of the Tom River and are connected by two road and one railway bridges.
The time here is Krasnoyarsk and relative to Moscow it is offset by 4 hours. Since 2014, a sixth time zone has been established in the region, which has increased the time difference with the capital to four hours.
There is a sharply continental climate and very cold winters, which, by the way, are also 2.5 months longer than the calendar frosts. Temperatures are below zero already at the end of October, and winter ends only in April. At the same time, summer is warm and humid, although it is 11 days shorter than the calendar year. In 2014, abnormal precipitation was recorded in early June, when wet snow fell throughout the territory.
Recent statistics have shown a decrease in atmospheric emissions from enterprises, which is good news. Of course, we cannot discount the growing number of cars in the city, which somewhat changes the main source of environmental pollution.
The science
On its territory, the Siberian Federal District has branches of three Russian academies of sciences: SB RAS, SB RAMS and SB RAAS. They include more than a hundred research organizations and a network of research and experimental stations. In the Siberian Federal District there are 7,767 daytime educational institutions (not taking into account evening ones), of which 411 are primary education, 410 are secondary education (of which 33 are non-state), 116 are higher education (not taking into account branches, of which 33 have the status of non-state). The largest number of higher educational institutions are concentrated in the Novosibirsk region (26), as well as in the Omsk (19) and Irkutsk (15) regions. For ten thousand inhabitants, the number of students and students in primary education institutions is 81 people (in the Russian Federation - 64 people), in secondary education institutions - 159 people (in the Russian Federation - 138 people), in higher education institutions - 429 people ( in the Russian Federation – 454 people).
City development
In 1926, the city was renamed and received its modern name Novosibirsk. It developed rapidly, which allowed A. Lunacharsky, who visited it in the late 20s, to call it “Russian Chicago.” During the Second World War it became a large industrial city. In addition to their enterprises, such as the aviation industry, enterprises from the central part of the USSR were evacuated here.
In 1937, the Altai Territory, Novokuznetsk and Tomsk regions were removed from the West Siberian Territory. Since 1943, the Novosibirsk region was formed with the regional center of Novosibirsk. In 1957, the Siberian Branch of the USSR Academy of Sciences was created. Academy Town was built on the outskirts of the city. The city becomes the largest scientific center not only in Siberia, but also in the country.
Healthcare
According to data for 2012, in the Siberian Federal District there are 197.6 thousand hospital beds, which is 102.6 beds per ten thousand residents (in the Russian Federation - 94.2 units); doctors of all specialties - 102.2 thousand people, based on ten thousand inhabitants - 53.1 doctors (in the Russian Federation - 51.2 specialists); paramedical personnel - 222.1 thousand people, based on ten thousand inhabitants - 115.3 people (in the Russian Federation - 107 people).
Culture and sports
The number of theater spectators in the formation is 254 people per thousand population. According to this indicator, the Siberian Federal District ranks third among the federal districts of Russia. Museums are visited by 373 people per thousand inhabitants (fifth place in the Russian Federation). The library stock of accessible institutions totals 5,883 copies per thousand population (also fifth place), and the one-time circulation of newspapers per thousand population is 772 copies (sixth place). The administrative formation has 34,508 sports institutions, of which 326 stadiums with stands for one and a half thousand or more seats, 21,039 flat sports facilities (fields and playgrounds), 12,575 gyms, 568 swimming pools. In addition, in the Siberian Federal District there are 8,324 health institutions for children.
Enterprises and work in Kemerovo
Perhaps city guests will be interested in employment opportunities. So, much more people in physical labor are needed here than humanities specialists.
You can find vacancies at industrial plants, work in the chemical and energy fields, and engage in machine construction and woodworking. In addition, Kemerovo is a concentration point for large enterprises. Most often, people seek to get a job at SDS-Holding, which covers almost all business areas from alcohol to engineering.
KPO Azot, which deals with chemical products and the production of agricultural fertilizers, is quite attractive for employment. There are almost always vacancies here. Specialists of a narrow profile are required at the LLC Production Association Khimprom, which is famous for the production of auto chemical goods for cars. Specialists are rarely required at Tokem LLC. Now it is the largest manufacturer of polymer materials.
Orton OJSC, which produces geosynthetic materials, is not particularly popular. Perhaps the low rating is due to low salaries and hard work. Mostly local residents work here, but migrants bypass society.
Kemerovo, by the way, is considered the scientific and educational center of the region, which is confirmed by the development of service and trade sectors. There are a lot of shopping centers in the city, so you can find not only work, but also entertainment. Visitors will find the Promenade shopping mall and the Greenwich shopping mall, but the Semyorka shopping mall is considered more modest. Well, it’s worth visiting the TSUM shopping center, which is common to all cities of the country.
Additional Information
Since May 12, 2014, the representative of the President of the Russian Federation in the Siberian Federal District has been Nikolay Evgenievich Rogozhkin. Before him, this position was held by Viktor Aleksandrovich Tolokonsky (since September 2010). Even earlier, the plenipotentiaries were Anatoly Vasilyevich Kvashnin (2004-2010), Leonid Vadimovich Drachevsky (2000-2004). The responsibilities of the authorized representative of the Siberian Federal District include organizing work on the implementation by authorities within the district of the main directions of foreign and domestic state policy; to monitor the implementation of government decisions; to ensure the implementation of the personnel policy of the Russian President.
Do you want to know any more information about the Siberian Federal District? The official website will help you with this. His address: sibfo.ru.