Irkutsk is one of the largest cities in eastern Siberia, considered a science city and having an ancient and rich history. Until the October Revolution of 1917, it was a merchant village that lived and developed from trade with China. Irkutsk is included in the UNESCO World Heritage List as one of the most historically significant cities in Russia.
How the city of Irkutsk developed, what the population was in it and how it changed over the years and according to the gender and age factor - we will analyze in detail in the article, based on the data provided by Rosstat.
Current data
For 2021, the following current figures and facts for the city of Irkutsk can be cited:
- The toponym of the name arose along the Irkut River, into which the Angara flows - and at the confluence of which a settlement was built, which gradually grew into a large city with developed hydropower, aircraft manufacturing, food industry, and science.
- Founded in 1661. The original purpose was a prison. In the vast majority of cases, convicts and political prisoners were sent here.
- Today the population of the city of Irkutsk is 623,562 people, which makes it the 5th largest city in Siberia.
- Today, the point includes the following districts: Kirovsky, Oktyabrsky, Sverdlovsky, Kuibyshevsky Leninsky districts.
- It is part of the Irkutsk region, of which it is a separate administrative municipal entity and the capital.
- President of the Russian Federation V.V. In 2021, Putin signed a decree that awarded the title of “City of Labor Glory.”
- The city is divided into left-bank and right-bank parts by the Angara River, approximately 300 m wide.
- Irkutsk has a sharply continental climate, which gives a difference in temperature between the summer and winter seasons of 70°C.
What is the population in Irkutsk
Currently, the city's population is 623,736 people. The density is thus 2251 people/sq. km. It ranks 22nd in terms of population among cities in the Russian Federation.
Before the collapse of the Soviet Union, new residents were constantly arriving in Irkutsk. Then, from 1991, the population began to decline. At that time, 641 thousand people lived in the capital of the Irkutsk region. In 1999, the population decline began to be felt more strongly. Then the migration outflow began, and the natural decline increased. This happened until 2009. Then the number of inhabitants began to increase again. Currently, the population of the city of Irkutsk is growing slowly but steadily.
Statistics by year
If we talk about the population of the city of Irkutsk, here is how it has changed over the past 170 years:
- In 1856, when the first statistical census was carried out, confirming 24,100 people.
- By the post-revolutionary year of 1923 it had increased to 88,264.
- In 1831 there were 113,215.
- By 1839 it had more than doubled - to 250.181.
- In 1956 it was 314,000.
- In 1962 - 385,000 people.
- Already in 1975, 516,000 people began to live here.
- By 1985 – 601,000.
- By 1990 - 582,000.
- In 1995, the number of living citizens decreased even further, resulting in a figure of 581,000.
- But for the 2000 calendar period, the composition here reached 593,700.
- In 2005 – 582,500.
- In 2010 – 587.891.
- In 2015 – 620.099.
- For 2021 – 623.479.
Over more than 170 years of history, the population has increased more than 25 times. True, at the same time it is worth noting that over the past 5 years, until 2021, it has remained virtually unchanged in number and density. The figure fluctuates around 623,000, showing periodic growth and then a short fall, within a few 100 people.
Irkutsk prison
The Angara River (according to legend, the daughter of a strict father - Lake Baikal) divides Irkutsk into two parts. Many centuries ago, the first trading settlements arose here, from where caravans went to China, Yakutia, Mongolia, Kamchatka and Alaska. The ancestors of the Yakuts and Buryats were the first to populate the territory of central Siberia. The city itself is young - it is 350 years old. In the 17th century, the development of Siberia by Russians began. Historians consider the construction of the Irkutsk fort in 1661 to be the founding of the city. Today, on the site of the fort there is a stone Church of the Savior.
The prison (a wooden structure made of planed logs, unlike the Kremlin, which was made of stone) was built on the site of the best arable land by the boyar's son Yakov Pokhabov. It was small, only 18 by 19 meters. After the fire, a new fort was built according to all the rules of fortifications, which existed until the beginning of the 18th century, when Irkutsk entered the Siberian province and became the residence of the Governor-General of Eastern Siberia. Today the residence houses the scientific library of the local university.
For three centuries, Irkutsk was considered the largest merchant city in Siberia. Until now, the central streets of the regional center are named in honor of merchant families. In parallel with trade, mining is carried out, and the first gold miners appear. Currently, up to 10 percent of all Russian gold reserves are mined here. After the construction of the Irkutsk State District Power Plant on Angara, the region becomes the largest supplier of electricity in Siberia. The defense industry and energy-intensive enterprises are developing.
About the city
If we talk directly about Irkutsk, today we can cite the following facts:
- The area is 277 sq. km.
- It is the largest formation in the region.
- The history begins with a fort, which was organized here from 1620 to 1650. Historians' versions differ somewhat on the exact date of its founding.
- Today, the city may be between 400 and 430 years old.
- In the immediate vicinity there is a reservoir and a local hydroelectric power station.
- The closest of the large settlements is Ulan-Ude, and of the million-plus cities - Krasnoyarsk.
- It is located on a flat area with slight hills, surrounded by forests of various types, as well as meadows and floodplains.
- On the territory and in the adjacent vicinity there are more than 40 parks, flower beds, groves, and protected arboretums.
- From an environmental point of view, the region is not favorable enough. Due to increased emissions from enterprises and industries of the electric power industry, the annual concentrations of formaldehyde, nitrogen oxides, benzopyrene and other harmful chemical compounds in the air are exceeded here.
- Another interesting fact is the specific drinking water. It comes here from a reservoir that is directly connected to Lake Baikal. However, since the water in it is close to distilled, that is, it has low mineralization rates, this negatively affects health. Regular use of it leads to the development of osteoporosis and other diseases. Today, there are several federal projects that are designed to bring mineralization standards to the required GOST levels. But, due to lack of funding, none of them has been implemented.
- Among the industries developed here are hydroelectric power stations, an aircraft plant, a heavy engineering industry, a relay plant, and the food industry.
- Transit tourism has been developed in Irkutsk, ensuring an influx of both Russians and guests from abroad to the territory of Lake Baikal.
- There are numerous vocational schools, technical schools, 6 universities and numerous branches here. Science is developed, which is represented by research institutes, departments of the academy, the Russian Geographical Society, scientific centers of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences and other organizations.
Geographical features
Irkutsk is located somewhere in the East Siberian region, on both sides of the Angara River. The closest city to it is Ulan-Ude, the distance to which is 439 km. Of the large million-plus cities, the closest is Krasnoyarsk. The distance to it in a straight line is 850 km. As for the distance to the capital of Russia - Moscow, it is 5200 km.
The relief of Irkutsk is flat and hilly. Landscape zone – forest-steppe. Near the city there is a reservoir of the same name. It is closed by the dam of the Irkutsk hydroelectric station.
Ethnic composition
The total population of the city of Irkutsk is represented not only by Russians, but also by other nationalities, which form the total population for 2010. This includes:
- Russians – more than 501,000.
- The second largest population are the Buryats - more than 12,000.
- Ukrainians and Tatars are present here in approximately the same percentage – about 5,000.
- The Azerbaijani, Kyrgyz, and Armenian diasporas are represented by residents - just over 2,000.
- The least numerous are Uzbeks, Tajiks, Belarusians, Tuvans and Jews. There are a little more than 1 thousand of them.
Demographic situation in the Irkutsk region and agglomeration
Appendix A.1. to the Concept of the Irkutsk agglomerationSee the complete Concept of the Irkutsk agglomeration here.
Irkutsk compared to other cities - trends of the 20th century
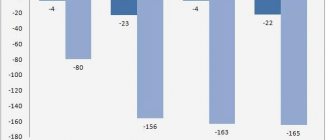
Irkutsk, as a major urban center in eastern Russia, has experienced rapid development since the end of the 19th century. and during this time it “increased” the population by 11.3 times (compared to the results of the 1897 census). However, in the context of rapidly progressing urbanization, as well as population movement from the west of the country to the east, this growth is comparable to the dynamics of changes in the population of other Russian cities: the growth rate of the urban population of Irkutsk is comparable to Moscow (10.0 times), but for the capital the starting point was population of more than 1 million people. Over the same period, the population of Yekaterinburg increased by 30.4 times, Krasnoyarsk - by 34.1 times, Khabarovsk - by 38.5 times. Novosibirsk has increased its population 11.6 times since 1926. (Fig. 1).
Figure 1
Population growth rates of some Russian cities in the 20th - early 21st centuries. (as a percentage of the previous date) * 1926 was taken as the base point.
In recent years, the population of Irkutsk has remained practically unchanged, while the population of Moscow has increased since the 1989 census. by 16.2%, Krasnoyarsk - by 5.9%, the population of Yekaterinburg and Novosibirsk remained virtually unchanged, and only Khabarovsk lost almost 4% of its population. All this allows us to talk about Irkutsk as an ordinary large city, which at the beginning of 2006. ranked 24th among Russian cities in terms of population
Irkutsk is more noteworthy as the center of the agglomeration of the same name
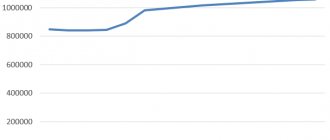
. The Irkutsk agglomeration actually began to take shape in the second half of the twentieth century. Back at the end of the 19th century, according to the 1897 census, the population of Irkutsk was 51 thousand people[1], and other settlements now included in the agglomeration were represented by small villages. However, by 1926 The city's population actually doubled, and by 1939 reached 250 thousand people. In 1951 Angarsk received the status of an urban settlement. By the time of the 1959 census. the population of the three districts of the region that form the current agglomeration (Irkutsk, Angarsk and Shelekhovsky together with cities) amounted to 581.5 thousand people. In 1962 Shelekhov received the status of a city (in 1959, the population of the town of Shelekhov numbered 13 thousand people). The change in the population of cities and districts of the region classified as part of the Irkutsk agglomeration is shown in Fig. 2.
Figure 2 Population of the Irkutsk region and areas included and not included in the Irkutsk agglomeration, 1959-2006, thousand people
By the time of the 1970 census. the population of the agglomeration increased to 757 thousand people (an increase from the last census data of 185.5 thousand people), by the 1979 census. - up to 901.8 thousand (144.8 thousand), by 1989, according to published data, the population was 1 million 10 thousand people. However, according to the results of population recalculations made from the 2002 census data, the population of the districts and cities forming the agglomeration did not exceed as of the 1989 census date. 970 thousand. The fact is that during the 1989 census. About 40 thousand people were assigned to Irkutsk, apparently the so-called. “special contingents” or the population of ZATO, which were “secret” in this way, according to the tradition of Soviet statistics (a recalculation of the population of Irkutsk was carried out in 1994, as a result, in 1995 published data showed a sharp decrease in the city’s population over the year - by 45.2 thousand . person, which did not happen in reality).
At the turn of the 1990s. the population of the agglomeration continued to grow, but in 1991-1993. it was slowly shrinking. Then growth followed again, as a result of which the population of the cities and regions included in the agglomeration reached its maximum size: by the beginning of 1999. it amounted to 987.7 thousand people (according to the census) or 991.2 thousand (according to previously published current population records). Since that time, the population of the Irkutsk agglomeration began to decline (Fig. 2).
It should be noted that the population of the cities and districts that make up the agglomeration has always grown faster than the population of the region. So, if in 1959 29.4% of the region's population lived in them, then at the beginning of 2006. - 38.1%. As can be seen in Fig. 2., from the very beginning of the 1990s, the total population of cities and districts of the region not included in the agglomeration has been declining, and the rate of this reduction in the mid-1990s was 20-25 thousand people per year, to date they have decreased to 12-14 thousand people per year.
Population census 2002 adjusted the population of the Irkutsk region downward, but this adjustment practically did not affect Irkutsk and the cities of the agglomeration. Population decline in other districts of the region in 2002. in the amount of 128 thousand people (Fig. 3) is the departure of the population during the intercensus period, not taken into account by the current accounting, primarily to other regions of the country. Such unregistered departure occurred both from cities and from metropolitan areas, but it was extinguished due to the influx of population from other areas of the region.
Rosstat proposed a methodology for adjusting data on annual population dynamics and migration growth for the intercensal period. Using this methodology, Irkutskstat carried out a recalculation of the population at the level of cities and districts of the region[2].
Figure 3
Change in the population of cities and districts of the Irkutsk region, included and not included in the Irkutsk agglomeration, according to current records and calculations from the 2002 population census, thousand people
Changes in the population of cities and districts included in the agglomeration, and others districts of the region are interconnected. Total for 1990-2005 the population of the agglomeration actually did not change (decreased by 6.7 thousand people), while at the same time the population of other cities and districts of the Irkutsk region decreased by 261.1 thousand people or by 14.3%. This is the population of a city like Angarsk. In fact, the entire population decline in the Irkutsk region observed by statistics was “thanks to” the regions.
What caused such dynamics of population decline? Natural decline
population in the Irkutsk region has been stable since 1993: since that time it has amounted to -135.8 thousand people (since 1990, the number of deaths has exceeded the number of births by 102.6 thousand people). The rest of the decline in the region's population (for 1990-2005 - 158.5 thousand people, or 60% of the population decline) is due to migration, primarily to areas of the country located to the west of the region.
Naturally, during the period of time under consideration, there was a migration exchange between the districts and cities included in the agglomeration and other settlements in the region, which developed in favor of the agglomeration. Population census data made it possible to realistically assess the components of population dynamics (Fig. 4).
Figure 4 Components of changes in the population of the Irkutsk agglomeration (taking into account recalculations from the results of the 2002 population census), thousand people
The dynamics of the components of population growth (decrease) in the Irkutsk region is presented in Fig. 5, which shows that maximum growth (both due to the processes of natural and mechanical movement of the population) was noted in the 1960s, then the population growth rate decreased. At the turn of the 1980s - 1990s. and in the early 1990s there was a migration outflow from the region, which in 1994-95. was replaced by an increase due to significant migration to the region from the CIS countries. In Fig. Figure 5 shows how insignificant this flow was in comparison with the data for 1960-1980. Then this flow dried up.
Figure 5
Components of the population dynamics of the Irkutsk region in 1989-2005[3]
* 1940-1980
— urban population It should be noted that when presenting data on the migration growth of the population of the region (and also, in other cases, districts and cities), we operate with official statistics, which receive information based on the development of sheets of statistical registration of migrants when registering at their place of permanent residence residence. These statistics do not take into account migrants registered at their place of stay, as well as those who live in cities and districts of the region without any registration. At the same time, these statistics do not take into account those who left the region (districts, cities) and did not change their place of permanent residence.
As already mentioned, in the Irkutsk region the excess of the number of deaths over the number of births has been noted since 1993, and the situation does not tend to change (Fig. 6). A natural decline was noted for both urban and rural populations. The total fertility rate (TFR) decreased from 2.243 (in 1990) to 1.446 (in 1995) and 1.255 (in 1999); by now (2005) it has increased to 1.406, which is significantly below the level of simple population reproduction. TFR of the urban population in 2005 was 1.302, rural - 1.908. The total fertility rate in the Irkutsk region is 0.1-0.2 children higher than the Russian average.
Figure 6 Born and died in the Irkutsk region, thousand people
Fertility indicators for the cities and regions that are part of the Irkutsk agglomeration do not differ fundamentally from the regional average indicators.
Mortality situation
The population is most generally characterized by the indicator of life expectancy (LE) at birth. In contrast to the situation with the birth rate, in the Irkutsk region there are significant differences from all-Russian data for the worse (Fig. 7). Despite the fact that life expectancy in Russia is extremely low for countries comparable in terms of socio-economic development, in the Irkutsk region life expectancy for men is 3.5-5.5 years below the Russian average, for women - 2.5-3.5 years. If in Russia the life expectancy of men at birth in 2005 approximately corresponded to this indicator in countries such as Yemen (59 years) and Myanmar (57 years) [4], then the life expectancy of men in the Irkutsk region (53.4 years) is at the level of Senegal (53 years) and Madagascar (53 years). The life expectancy of men is lower only in sub-Saharan African countries significantly affected by the HIV/AIDS epidemic.
Figure 7 Life expectancy at birth for men and women in the Irkutsk region in comparison with all-Russian data (years)
The difficult situation with mortality in the Irkutsk region is largely due to the specific causes of death. So, in 2005 in the Irkutsk region, the mortality rate from infectious and parasitic diseases was almost 2 times higher than the Russian average, in particular: from respiratory diseases - 1.4 times; from external causes, injuries and poisoning - 1.55 times. The mortality rate from suicide in the region is significantly higher - 1.7 times, from alcohol poisoning - 1.55 times higher than the national average[5]. These causes most often cause death among the young male population.
In the future, the situation in the Irkutsk region will be complicated by the high (in comparison with the Russian average) prevalence of HIV/AIDS (3.3 times). The HIV infection rate of the entire population of the Irkutsk region was 0.9%, while the Russian average was 0.2%. According to the forecast, the number of HIV-infected people in the region by 2010 will be will reach 35 thousand,[6] which will be 133 people per 100 thousand population. Among people of active reproductive age, the proportion of people infected and suffering from AIDS will be even higher. As a result, the number of children born to HIV-infected mothers will increase.
The Irkutsk region has a higher infant mortality rate than the Russian average (12.5 per 1,000 live births versus 11.0), although this gap has been narrowing in recent years. In addition, the cities that are part of the agglomeration have infant mortality rates below the regional average (in Angarsk in 2005 this figure was 4.6 per 1000 births)[7].
Overall mortality rates in Irkutsk, Angarsk and Shelekhov are slightly lower than the regional average, which is most likely the result of better organization of the health care system in the cities that form the agglomeration.
Demographic processes in recent years have seriously affected the age and sex structure
population of the region. The most significant change is associated with the general aging of the population: if in 1989. the average age of the region's population was 31.6 years (the entire population of Russia is 32.8 years), then by 2002. it increased to 35.4 years (Russia - 37.1 years). The average age of the male population of the region has changed to a lesser extent - from 29.7 years to 31.1 years (Russia - 30.5 and 34.1 years) due to the growth rate of mortality among young men, which is ahead of the Russian average. Those. The region's population continues to remain relatively younger, but this is largely due to negative mortality trends.
The aging of the population of the region as a whole and of the cities and districts that form the agglomeration is associated, first of all, with a reduction in the proportion of children. The age-sex pyramids presented in Fig. 8 give a general idea of the specifics of aging processes in regions and cities included and not included in the agglomeration.
Figure 8 Age and sex composition of the population of cities and districts included and not included in the agglomeration, according to the population censuses of 1989 and 2002. [8]
From Fig. 8 and table. 1 shows that the age structure of the population of the cities and districts included in the agglomeration has undergone less serious changes than the population of other years and districts of the region. Thus, the number of children aged 0-4 years in the agglomeration in 2002. amounted to 55.0% of the 1989 level, and in other regions and cities - 47.3%.
Table 1 Population by 5-year age groups in the Irkutsk region and its parts according to the 1989 and 2002 censuses, people
| 1989 | 2002 | |||||
| Irkutsk region | agglomeration | other areas | Irkutsk region | agglomeration | other areas | |
| Total | 2824920 | 1010004 | 1814916 | 2581705 | 975560 | 1606145 |
| 0-4 | 269557 | 83977 | 185580 | 133886 | 46184 | 87702 |
| 5-9 | 256869 | 79809 | 177060 | 142267 | 48620 | 93647 |
| 10-14 | 231972 | 73545 | 158427 | 215986 | 69821 | 146165 |
| 15-19 | 207281 | 83646 | 123635 | 242594 | 101307 | 141287 |
| 20-24 | 193366 | 78456 | 114910 | 219707 | 94984 | 124723 |
| 25-29 | 249705 | 87174 | 162531 | 203095 | 82487 | 120608 |
| 30-34 | 261748 | 89548 | 172200 | 175849 | 69886 | 105963 |
| 35-39 | 241274 | 85130 | 156144 | 173190 | 64170 | 109020 |
| 40-44 | 146794 | 57370 | 89424 | 215042 | 75106 | 139936 |
| 45-49 | 152168 | 56886 | 95282 | 204750 | 71221 | 133529 |
| 50-54 | 172140 | 63544 | 108596 | 177827 | 64983 | 112844 |
| 55-59 | 136123 | 48726 | 87397 | 86747 | 34697 | 52050 |
| 60-64 | 123003 | 46327 | 76676 | 128402 | 49199 | 79203 |
| 65-69 | 65975 | 26469 | 39506 | 96744 | 36514 | 60230 |
| 70 | 116945 | 49397 | 67548 | 162799 | 64919 | 97880 |
| Changes in population size by individual age groups in 2002 compared to 1989: | ||||||
| Thousand Human | % | |||||
| Irkutsk region | agglomeration | other areas | Irkutsk region | agglomeration | other areas | |
| Total | -243,2 | -34,4 | -208,8 | 91,4 | 96,6 | 88,5 |
| 0-4 | -135,7 | -37,8 | -97,9 | 49,7 | 55,0 | 47,3 |
| 5-9 | -114,6 | -31,2 | -83,4 | 55,4 | 60,9 | 52,9 |
| 10-14 | -16,0 | -3,7 | -12,3 | 93,1 | 94,9 | 92,3 |
| 15-19 | 35,3 | 17,7 | 17,7 | 117,0 | 121,1 | 114,3 |
| 20-24 | 26,3 | 16,5 | 9,8 | 113,6 | 121,1 | 108,5 |
| 25-29 | -46,6 | -4,7 | -41,9 | 81,3 | 94,6 | 74,2 |
| 30-34 | -85,9 | -19,7 | -66,2 | 67,2 | 78,0 | 61,5 |
| 35-39 | -68,1 | -21,0 | -47,1 | 71,8 | 75,4 | 69,8 |
| 40-44 | 68,2 | 17,7 | 50,5 | 146,5 | 130,9 | 156,5 |
| 45-49 | 52,6 | 14,3 | 38,2 | 134,6 | 125,2 | 140,1 |
| 50-54 | 5,7 | 1,4 | 4,2 | 103,3 | 102,3 | 103,9 |
| 55-59 | -49,4 | -14,0 | -35,3 | 63,7 | 71,2 | 59,6 |
| 60-64 | 5,4 | 2,9 | 2,5 | 104,4 | 106,2 | 103,3 |
| 65-69 | 30,8 | 10,0 | 20,7 | 146,6 | 138,0 | 152,5 |
| 70 | 45,9 | 15,5 | 30,3 | 139,2 | 131,4 | 144,9 |
Studying the dynamics of the age-sex composition using the method of moving ages also allows us to see that the cities and regions included in the agglomeration have attracted a young population in recent years. If we compare the population aged 0-4 years and 5-9 years in 1989. and, respectively, 15-19 and 20-24 years old in 2002. (14 years passed between censuses), it is clear that in the agglomeration the increase in the population of these cohorts was approximately 20% (although it could only decrease due to natural causes). Probability of “survival” from age 1 to 15 in 1999 in Russia it was 98.9% for men, 99.3% for women; at the age from 5 to 20 years - 98.3% and 99.2%, respectively[9]. On the contrary, the population of the corresponding ages in other areas of the region decreased by 25-30% over the specified period. This is the result of the redistributive influence of migration, incl. educational And this is one of the main “advantages” of the agglomeration, which is already visible: its ability to attract a young active population from other areas of the region.
Positive aspects of the change in the age structure of the population of the Irkutsk agglomeration include an increase in the proportion of the population aged 15-24 years (Fig. 9) - this is a well-known all-Russian trend. However, this situation will very soon change to the opposite, because This age will include generations born in the 1990s. This will inevitably reduce the number of potential applicants to universities and secondary vocational education institutions.
Figure 9 Distribution of the population by 5-year age groups in cities and metropolitan areas and other areas of the Irkutsk region in 1989 and 2002, %
According to the latest demographic forecast published by Rosstat[10], in Russia the birth rate is expected to increase (the total fertility rate will increase to 1.64 by 2025) and mortality will decrease (life expectancy at birth will increase by 2.6 years). Population growth will also increase due to external migration (up to 438 thousand people per year by 2025). At the same time, the population below the working age will grow slightly, the working age population will decrease, and the population older than the working age will increase at a fairly high rate.
According to this forecast, the population of the Irkutsk region will decline, and at a faster rate than the population of the country as a whole (Fig. 10). At the same time, the forecast is based on the premise that the total fertility rate in the Irkutsk region will be higher than in the country as a whole (1.782 versus 1.649 in 2025), i.e. the current “separation” of the region will remain.
However, a higher mortality rate will also remain: life expectancy at birth in the Irkutsk region for men will be in 2025. 57.7 years, for women - 72.0 years (in Russia - 61.9 and 74.8 years, respectively). Those. the forecast is based on the premise of a continuing gap in the mortality rates of the population of the Irkutsk region with the country as a whole.
Figure 10 Forecast of population dynamics in Russia and the Irkutsk region, incl. working age population (2007 = 100%)
An important condition included in the forecast: the migration outflow of the population from the Irkutsk region will remain in the amount of 5-6 thousand per year (-20/-30 people per 10 thousand population), while in Russia as a whole there will be a migration influx, increasing from 10 to 30 per 10 thousand population.
Thus, it is clear that it is possible to influence the demographic situation in the region, first of all, by fully countering the abnormally high mortality rate and creating conditions for reducing the migration outflow of the population to other regions of the country. It may be possible to slightly accelerate the growth of the birth rate in the region (for example, to reach a birth rate of 1.8 children per woman not by 2025, but by 2015), but these measures will have an effect on the region’s economy no earlier than in 20 years. Moreover, if nothing is done to maintain the population, measures to support the birth rate will be meaningless - both from a social and economic point of view.
[1] Population of Russia for 100 years (1897-1997): Stat. Sat. / Goskomstat of Russia. —M., 1998. p. 58
[2] Retrospective population by cities and districts of the Irkutsk region in 1989-2002. Statistical collection. Irkutskstat, 2006.
[3] Source
: Population of Russia for 100 years (1897-1997): Stat. Sat. / Goskomstat of Russia. -M., 1998; Data from Rosstat of Russia
[4] All countries of the world. “Population and Society” - Information Bulletin of the Center for Economic and Social Sciences of the Institute of Economic Forecasting of the Russian Academy of Sciences No. 93, August 2005.
[5] Main performance indicators of medical institutions in the Irkutsk region for 2005. State Healthcare Institution of the Irkutsk Region. Irkutsk, 2006, p.11.
[6] According to the forecast of the Department of Health of the Irkutsk Region
[7] Main performance indicators of medical institutions in the Irkutsk region for 2005. State Healthcare Institution of the Irkutsk Region. Irkutsk, 2006, p.9.
[8] Sources
: Sex and age characteristics of the population of the region (according to the 1989 population census). Irkutsk, Irkoblstat, 1990; Age, sex composition and marital status in the Irkutsk region, including the Ust-Orda Buryat Autonomous Okrug. Part 1, Irkutsk, Irkutskstat, 2004.
[9] Demographic Yearbook of Russia 2002. Statistical collection. M., Goskomstat of Russia, 2002
[10] Estimated population of Russia until 2025 (Statistical Bulletin). M.: Federal State Statistics Service, 2005.
Gender and age
As for age indicators, here is how many residents live in the city of Irkutsk according to these parameters:
- From 0 to 4 years – 44.766.
- From 5 to 9 years – 43.462.
- From 10 to 14 – 34.321.
- From 15 to 19 – 30.964.
- From 20 to 24 – 31.726.
- From 25 to 29 – 59.134.
- From 30 to 34 – 67.122.
- From 35 to 39 – 53.605.
- From 40 to 44 – 44.026.
- From 45 to 49 – 38.998.
- From 50 to 54 – 30.612.
- From 55 to 59 – 33.254.
- From 60 to 64 – 32.198.
- From 65 to 69 – 29.070.
- From 70 to 74 – 20.512.
- From 75 to 79 – 10.894.
- From 80 to 84 – 12.453.
- From 85 to 89 – 4.316.
- From 90 to 94 – 1.765.
- From 95 to 99 – 303.
- More than 100 years – 61.
As for gender distribution, here are the statistics in the city of Irkutsk in this regard:
- Men of all ages live here as of 2021 - 277,683.
- Women, regardless of age – 345,879.
Information of the Irkutsk region
Sights and culture of Irkutsk
Local residents advise starting to explore the city from the central square.
Based on the number of renamings, it can qualify for inclusion in the Guinness Book of Records. Here are some of its names:
- Kremlevskaya;
- Spasskaya;
- Bogoroditskaya;
- Epiphany;
- Gostinodvorskaya;
- Parade area;
- Speransky;
- Third International;
- named after Kirov.
Today the central square is called Kirovskaya, but local residents say: “Let's go to the square.” Here is a beautiful city park, administrative buildings of Irkutsk, and the Angara Hotel.
A monument to Alexander Vasilyevich Kolchak was recently erected in the city - from the high bank of the Angara, the majestic figure of the admiral looks at the city. At the foot of the monument, a Red Army soldier and a White Guard officer crossed arms - a symbol of respect for the tragic hero of that era, a brilliant commander. The admiral was shot not far from the place where the monument is located, and his body was lowered under the ice near the Znamensky Convent.
Irkutsk has many attractions associated with the stay of the exiled Decembrists here.
The most famous is the Volkonsky house. The hero of the Patriotic War of 1812, at the end of his exile, received permission to live in Irkutsk and built a house with bay windows - something previously unseen by Siberians. Sergei Grigorievich himself supervised the construction of the house. After the Volkonskys left, the house was rented out, and then it was bought by an Irkutsk merchant, who set up a craft shelter for orphan boys. Today the Volkonsky house is an architectural monument; one of the halls of the Decembrist Museum is located here. In addition to the excursion program, the museum hosts literary and musical evenings, balls and celebrations.
Townspeople often come to the grave of Ekaterina Ivanovna Trubetskoy, the first of the wives who followed their husbands to Siberia. The princess, born French, did not live two years before the amnesty of the rebels. Here, under a simple stone, lie the three young children of the Trubetskoys. In the house of the Trubetskoy princes, the atmosphere of that historical era is recreated; the second hall of the Decembrist Museum is located here.
When visiting Irkutsk, visit the Lace House, which has worldwide fame. The former house of the merchant Shastin is one of the few buildings made in the Russian Baroque style: with intricate turrets, wooden columns, and elegant wood carvings. After restoration, the European representation is located here. The merchant estates received a new name - the House of Europe. Today it has become the hallmark of the city.
The open-air architectural and ethnographic museum “Taltsy” is open seven days a week. It is here that you can get acquainted with the culture and heritage of all the nationalities that inhabited the city at different times:
- Evenks;
- Yakuts;
- Buryat;
- tofalar;
- Russians.
In the evening, we recommend visiting the local drama theater or the halls of the regional philharmonic society, and listening to organ music in the Polish church.
The cultural and spiritual life of Irkutsk is rich and multifaceted. On the posters you will find exactly what interests you.
Migration
If we talk about resettlement, the following figures are given for 2021:
- The number of arrivals is about 43,000.
- The number of those who left is 46,000.
Migration of the Irkutsk region
Thus, it is necessary to take into account that despite a fairly developed infrastructure and functioning industrial enterprises, numerous universities, cultural and other entertainment institutions, some of the townspeople are trying to move. Moreover, some move within the country, while others move to other states.
Irkutsk is the capital of a region with a rich history
Irkutsk is only in third position in terms of territory size, but in terms of the number of residents it is the undisputed leader with 623,869. The population of the agglomeration is even larger: according to information for 2018, it exceeds 1.1 million.
Since its foundation in the second half of the 17th century, it has played an important role in the life of the region. The merchant city had strong trade relations with China, the central and eastern regions of the country, and later repeatedly acted as a zone of exile. It is included among the historical settlements of Russia, and also boasts an abundance of attractions, mostly concentrated in the old center. Irkutsk is a student city, a major transport hub of the region and an important economic center, where many enterprises of all-Russian importance operate, including the largest Russian company in the energy sector, Irkutskenergo.