The Arkhangelsk region is the largest in the Russian Federation. It is larger in size than Madagascar and Italy. It has a rather harsh climate, as it is washed by the Arctic seas. Most of the territory is the Far North. The Arkhangelsk region also belongs to the northernmost point of Russia and the easternmost point of Europe.
The population of the region, according to the latest data for 2021, is 1 million 144 thousand people. The region has a surprisingly low population density, as there are approximately 2 people per 1 km². This fact is easily explained: most of the territory is uninhabitable. As of 2021, the urban population is 78.7%. People are constantly leaving the region. Negative dynamics of population growth have been observed since 1990.
The list of different nationalities in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation is as follows:
- Russians - 95.6%;
- Ukrainians - 1.41%;
- Nenets - 0.7%;
- Belarusians - 0.5%;
- Komi - 0.4%.
The Arkhangelsk region is a very promising region in terms of industrial development. Here is the largest diamond mine in Europe and one of the largest in the world. Quite a large amount of oil, gas, and huge peat deposits have been found in the region. The largest gypsum deposit in the Russian Federation is located in these parts.
The Arkhangelsk region attracts not only its wealth of natural resources, but also the amazing beauty of its taiga forests. They occupy a little more than half of the entire territory. Nature is under state protection: people are attracted to the region by the Russian Arctic and Onega Pomorie national parks.
Arkhangelsk is a small and important city
Arkhangelsk is the largest Russian city located in the northern regions. It was founded at the end of the 16th century by order of Ivan the Terrible. It was successively part of the Russian Kingdom, then the Russian Empire, then the USSR, and now the Russian Federation. The city is located approximately 35 km from the White Sea, on the banks of the Northern Dvina River. This location largely predetermined its historical development: Arkhangelsk was known for a long time thanks to monks and merchants who actively developed trade along the northern routes.
After the collapse of the USSR, the population has been constantly declining. These rates began to decrease since 2007 due to the fact that mortality began to decline and the birth rate increased. Living conditions improved, people began to stay here. By nationality, the majority of residents in the city are Russian.
Now in Arkhangelsk there is a certain demographic advantage: 55% of women and, accordingly, 45% of men. Local authorities are actively involved in various programs to attract migrants, including from abroad, to solve this problem.
Novodvinsk - history of the city
Paper was born at the center of the main technological discoveries made by mankind before the advent of the modern era, in the Far East, where the compass, gunpowder, type, porcelain, etc. were invented. The production of paper is usually associated with the name of the Chinese Cai Lun and dates back to 105 AD. However, paper began to be produced in China earlier; during archaeological excavations near the dead city of Khara-khoto (PRC), scraps of paper sheets were found. They investigated and found that the paper was made in the 2nd century BC. The merit of Tsai Lun can be considered the process of paper production: Tsai Lun crushed mulberry fiber, wood ash, rags and hemp. He mixed all this with water and laid the resulting mass on a mold, and through dehydration (drying) he obtained durable sheets of paper.
Paper was imported to Russia from Byzantium in the 14th century. The production of its own paper in Russia appeared in the middle of the 16th century under Tsar Ivan the Terrible. During the reign of Peter I the Great, the foundations were laid for the spread of education in Russia. Peter's decrees introduced compulsory education for nobles and clergy. Educational institutions began to appear, the first Russian newspaper was founded, and translations of many books into Russian appeared. Thanks to the demand for book printing, a powerful impetus was given to the development of paper production in Russia. Paper consumption at the end of the 17th century increased from 8 thousand sheets to 50 thousand sheets. Under Peter I, new printing houses were created, in which, from 1700 to 1725, 1,312 book titles were printed, which is twice as many as in the entire previous history of Russian book printing. In the 18th century, by decree of Peter I, paper mills were built near Moscow, St. Petersburg and other places. The material (raw material) for making paper was flax, hemp and cotton fibers obtained from rags. The beginning of machine paper production in Russia should be considered the year 1817, when the first paper-making machine was installed at the Peterhof paper mill.
Arkhangelsk, the center of the Russian North, starting from the second half of the 16th century, was a major center of the emerging all-Russian market, a place where large capitals were formed in trade, and then in industry. For a long time, the river route, laid through Vologda along the Sukhona and Northern Dvina to Arkhangelsk, and from there to foreign countries, attracted the largest Russian entrepreneurs like a magnet. One of these entrepreneurs were Arkhangelsk merchants Andrey Ivanovich Stukachev and Ivan Yakovlevich Demidov. In 1815, merchant of the 3rd guild Ivan Demidov decided to build a paper mill and sawmill near the village of Mechka. For these purposes, he bought land on the left bank of the Mechka-Poloy watercourse (the bed of the Northern Dvina River) from the merchant of the 1st guild Stukachev. In 1820, on the basis of a chain factory, Demidov opened a paper manufactory. The raw materials were rags collected in Arkhangelsk and its environs; the glue used in production was prepared directly at the factory from deer antlers and leather. Sandalwood for coloring paper was obtained from abroad. Alum was used to bleach the mass. Demidov's factory produced writing paper, blue and white sugar paper, wrapping paper and tea paper. On average, the paper factory produced 100–150 reams of paper per month, each containing 24 sheets. The factory existed for 45 years, producing paper until 1865. In January 1871, Demidov's paper manufactory completely ceased to exist. But it all ended only to begin again, and on a completely different scale. After 63 years, in these parts they started talking again about the production of the paper industry, and so the construction of a large plant for the production of sulfite pulp “Arkhbumstroy” (Arkhangelsk Pulp and Paper Mill) was started.
Foundation of the city
The first working day of construction of the Arkhangelsk pulp mill is officially considered April 7, 1935. At the beginning of May, builders laid out a forge and built a warehouse. And after the arrival of the first barge with lumber, they began to build a temporary construction camp. At that moment, 50 people were already working on the site. The news of the construction of a giant plant gave people strength; the builders continued to work tirelessly. The number of workers arrived: 231 people were hired in July, 240 in August, and 429 workers at the construction site in November. Regional newspapers such as Pravda Severa published advertisements inviting people to a new all-Union communist construction site. By the winter of 1935, the enthusiasm of the builders began to fade; difficult working conditions affected them; there were no mechanisms, no construction equipment; the tools of the builders’ labor were an axe, a shovel and a wheelbarrow. The logs were cut by hand using rip saws. People worked in mosquito nets, mosquitoes gave no rest for a minute, most of the sawyers lived right there in tents. Mosquitoes, a humid climate, and severe frosts in winter forced many builders to leave the construction site. In December 1935, for every 107 people who arrived, there were 337 people who left. The implementation of the construction program was unsatisfactory; construction work was carried out much behind schedule. At the beginning of 1938, another inspection of the construction site revealed a significant lag in construction work and concluded that it was impossible to put the enterprise into operation on time. The construction management had to raise the issue with the Council of People's Commissars about opening a prison camp at the construction site.
Construction of "Arkhbum" Construction of "Arkhbumkombinat" July 18, 1939
Arkhangelsk Pulp and Paper Mill Arkhangelsk Pulp and Paper Mill today
By order of July 10, 1938, a forced labor camp was organized, the management of the camp was directly subordinate to the NKVD Gulag in Moscow. This is how Mechkostroy was formed (as part of the Arkhlag). Housing construction began hastily at the construction site in May. Arriving prisoners were housed 200-300 people in one barracks. Before going to work in the paper mill area, a general formation of barracks residents took place in the Mechkostroy sections. In one row stood dispossessed peasants, repressed intellectuals, engineers and criminals. All these people, so different from each other, were then united by only one word - Archlag. When the construction of the plant was transferred to the jurisdiction of the People's Commissariat of Internal Affairs, a new deadline was set for the launch of the enterprise. According to the order of N.I. Yezhov, the plant should be put into operation in the fourth quarter of 1939. In March 1939, a commission of the Arkhangelsk City Party Committee was sent to the construction site, which concluded that the Arkhangelsk Paper Mill was not ready to start up in 1939. In connection with this, the Gulag approved a new plan for the commissioning of all structures of the plant and workers' settlement for 1940. On April 26, 1941, by the Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR, according to which Arkhbum was officially assigned a new status. A settlement near the sulfite pulp mill named after K.E. Voroshilov, which received the name of Stalin’s People’s Commissar of Defense in the fall of 1936, was classified as a worker and became known as the village of Voroshilovsky. At this time, 10,000 people lived in the village, not counting the Arkhlag prisoners. 83 residential buildings were built, there was a secondary school, a club with 400 seats, a library, a bakery, a store, a canteen, and a kindergarten. On May 12, 1941, a village council of 11 deputies was formed. During the Great Patriotic War of 1941-1945, the plant developed a new type of product: anti-mustard paper “PIK” - very strong, dense, impregnated with a special solution that did not allow gases to pass through. On November 25, 1941, the bureau of the regional committee of the All-Union Communist Party adopted a resolution “On the production of grenades at Arkhbumstroy.” At the plant, the issue of manufacturing skis, shovels, fire helmets, and tips for tent frames from production waste was resolved. The only sewing workshop in the village was engaged in sewing short fur coats, mittens and covers for shovels. In the fall of 1942, the pressing shop was put into operation. Its product was the powder mass, which constituted the contents of the gunpowder. From the APPM it was sent to a number plant, where gunpowder was made from it. The workshop was strictly classified. On January 8, 1957, the village of paper workers received a new name - the village of Pervomaisky, Isakogorsk district of the city of Arkhangelsk.
The city is located on the left bank of the Mechka-Polaya channel of the Northern Dvina River, 8.5 km from the Isakogorka railway station, 10 km from the M8 highway, 25 kilometers south of the city of Arkhangelsk.
Like other large enterprises of the USSR, the Arkhangelsk Pulp and Paper Mill took part in foreign economic activity. In particular, he collaborated with the Dunaujváros Pulp and Paper Mill (Hungary) and the Czechoslovakian enterprise from Banská Bystrica on scientific and technical research and improvement of the production of pulp, paper and cardboard. In December 1971, the State Committee for Science and Technology under the Council of Ministers of the USSR and the French concluded a cooperation agreement. The lead enterprise in this agreement was the Arkhangelsk Pulp and Paper Mill. From September 13 to 15, 1977, a Labor Friendship Watch was held at the Arkhangelsk Pulp and Paper Mill, in which workers from the pulp and paper industry from Bulgaria, Hungary, the German Democratic Republic, Poland, Romania and Czechoslovakia took part. In the 70s, preparation of project documentation for the expansion of the city of wallets was carried out. The possibility of mass construction of multi-storey buildings was explored. On November 24 (considered the date of birth of the city of Novodvinsk), 1977, by the Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR, the village of Pervomaisky was transformed into the city of regional subordination of Novodvinsk.
Attractions:
A park on the banks of the Mechka-Hollow channel of the Northern Dvina River. The central alley along the 50th Anniversary of October street. 3 kilometers from Novodvinsk there is a ski resort "Mechka" Church of the Descent of the Holy Spirit. Church of the Intercession of the Mother of God.
Novodvinsk is a mono-industrial city. The population as of 2014 is 39,937 people. The city-forming plant is the Arkhangelsk Pulp and Paper Mill, one of the leading enterprises in the timber industry. Novodvinsk is a city of regional subordination. The fourth largest city in the Arkhangelsk region.
Materials used in the text:
History of paper and paper production - A.P. Balachenkova St. Petersburg Passing the boundaries of eras, 1940–2010 N.A. Kosheleva, Arkhangelsk municipal formation "CITY OF NOVODVINSK"
Severodvinsk is a young city
Severodvinsk is a fairly young city in the region, as it was founded in the first half of the last century. Development was largely carried out by the USSR. At the moment it is officially recognized as part of the Far North. According to 2021 data, the population is 183 thousand people.
About 10 years ago we decided to develop the city as a science city. This concept was supposed to be successfully implemented before 2010, but in the end it was only partially realized. As part of the strategic development, the city administration managed to attract approximately 40 billion rubles to maintain scientific and industrial potential. The city is now in a state of crisis, although the situation is gradually improving.
Kotlas is a city with a noticeable population increase
Kotlas is one of the few cities in the Arkhangelsk region where a positive trend towards population growth has been observed in recent years. According to data for 2021, it amounted to 61.8 thousand people. The city-forming enterprise is the local railway. It provides approximately 45% of all employment. Salary payments here are quite stable and higher on average than in the city, as well as in its environs. Population growth occurs due to the attraction of people from smaller settlements in the region.
Kotlas is a city located in a territory equated to the Far North. It has a moderately cold climate. For relocation, it is suitable for those who are accustomed to the appropriate climatic conditions.
Novodvinsk
(Arhangelsk region)
OKATO code:
11415
Founded:
1936
Urban settlement since:
1941
City since:
1977 City of regional subordination
The city was formerly called:
| Voroshilovsky | 1941 | 1957 |
| Pervomaisky | 1957 | 1977 |
| Telephone code (reference phone) | |
| 81852***** | 43-6-85 |
Deviation from Moscow time, hours:
0
Geographic latitude:
64°25′
Geographic longitude:
40°49′
Altitude above sea level, meters:
20 Sunrise and sunset times of the Sun and Moon in the city of Novodvinsk
Novodvinsk is a city with affordable housing
The city is located 20 km from Arkhangelsk and has similar nature and climate, but with more pronounced continental features. The population here is attracted mainly by the availability of housing. The number of residents has been constantly decreasing in recent years.
As of 2021, the total population was 38.7 thousand people. Moreover, more than 97% consider themselves Russian. In terms of religion, atheists dominate, with Orthodox Christians in second place. There is every reason to believe that the dynamics of population growth will continue to be negative. According to a number of indicators, Novodvinsk is the most polluted city in Russia. A very large number of thyroid diseases also indicates the presence of a serious problem.
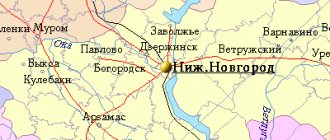
Map
| Novodvinsk: maps |
Novodvinsk: photo from space (Google Maps) Novodvinsk: photo from space (Microsoft Virtual Earth)
| Novodvinsk. Nearest cities. Distances in km. on the map (in brackets along roads) + direction. Using the hyperlink in the distance , you can get the route (information courtesy of the AutoTransInfo website) | |||
| 1 | Arkhangelsk | 20 (17) | NW |
| 2 | Kholmogory | 45 (52) | SE |
| 3 | Severodvinsk | 50 (60) | Z |
| 4 | Onega | 143 (250) | Z |
| 5 | Savinsky | 168 (294) | YU |
| 6 | Karpogory | 181 (309) | IN |
| 7 | Peaceful | 185 (320) | YU |
| 8 | Plesetsk | 191 (324) | YU |
| 9 | Bereznik | 197 (274) | SE |
| 10 | Severonezhsk | 209 () | YU |
| 11 | Mezen | 225 (477) | NE |
| 12 | Leshukonskoe | 241 (346) | IN |
| 13 | Solovetsky | 251 () | Z |
| 14 | Shenkursk | 277 (384) | YU |
a brief description of
The city is located on the left bank of the river. Northern Dvina, 11 km from the railway. Isakogorka station, 20 km south of Arkhangelsk.
Territory (sq. km): 41
Information about the city of Novodvinsk on the Russian Wikipedia site
Historical sketch
It was founded in 1936 near the village of Mechki as a settlement at a pulp and paper mill and was originally called Mechkostroy.
Since April 26, 1941, the working village of Voroshilovsky. In 1957 it was renamed Pervomaisky. He was a member of the Arkhangelsk City Council (Isakogorsky district).
On November 24, 1977, the village of Pervomaisky was reorganized into the city of Novodvinsk.
Municipal indicators
| Index | 2001 |
| Demography | |
| Number of births, per 1000 population | 9.5 |
| Number of deaths, per 1000 population | 12.8 |
| Natural increase (decrease), per 1000 population | -3.3 |
| Standard of living of the population and social sphere | |
| Average monthly nominal accrued wages, rub. | 5632 |
| Average housing area per inhabitant (at the end of the year), sq.m. | 17 |
| Number of preschool institutions, pcs. | 14 |
| Number of children in preschool institutions, thousand people | 2.3 |
| Number of daytime educational institutions (at the beginning of the school year), pcs. | 9 |
| Number of students in daytime educational institutions, thousand people | 5.6 |
| Number of doctors, people. | 204 |
| Number of nursing staff, people. | 585 |
| Number of hospital institutions, pcs. | 1 |
| Number of hospital beds, thousand units | 0.4 |
| Number of medical outpatient clinics, pcs. | 1 |
| Capacity of medical outpatient clinics, visits per shift, thousand units. | 1.4 |
| Number of registered crimes, pcs. | 1126 |
| Persons who committed crimes were identified, persons. | 444 |
| Economy, industry | |
| Number of enterprises and organizations (at the end of the year), pcs. | 397 |
| Construction | |
| Volume of work performed by type of activity “Construction” (until 2004 - volume of work performed under construction contracts), million rubles. | 95.3 |
| Commissioning of residential buildings, thousand sq.m. of total area | 3.3 |
| Commissioning of residential buildings, apartments | 53 |
| Commissioning of preschool institutions, places | 0 |
| Commissioning of educational institutions, places | 0 |
| Commissioning of hospital facilities, beds | 0 |
| Commissioning of outpatient clinics, visits per shift | 0 |
| Transport | |
| Number of bus routes (in intracity traffic), pcs. | 1 |
| Number of passengers transported by buses per year (in intracity traffic), million people. | 0.3 |
| Connection | |
| Number of residential telephone sets of the city public telephone network, thousand units. | 10.3 |
| Trade and services to the population | |
| Retail trade turnover (in actual prices), million rubles. | 765.8 |
| Retail trade turnover (in actual prices), per capita, rub. | 15660 |
| Public catering turnover (in actual prices), million rubles. | 71.3 |
| Volume of paid services to the population (in actual prices), million rubles. | 264.9 |
| Volume of paid services to the population (in actual prices), per capita, rub. | 5416.8 |
| Volume of household services to the population (in actual prices), million rubles. | 34.7 |
| Volume of household services to the population (in actual prices), per capita, rub. | 710.7 |
| Investments | |
| Investments in fixed assets (in actual prices), million rubles. | 886.8 |
| Share of investments in fixed assets financed from budgetary funds in the total volume of investments, % | 3.4 |
Data sources:
- Regions of Russia. Main characteristics of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation: statistical collection. Goskomstat of Russia. - M:, 2003.
Economy
The leading enterprise of the city is the Arkhangelsk Pulp and Paper Mill. Factory of reinforced concrete products, furniture factory.
Main enterprises
PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY
OJSC "Arkhangelsk Pulp and Paper Mill"
163901, Arkhangelsk region, Novodvinsk, st.
Melnikova, 1 Offers:
writing paper, wrapping paper, label paper, corrugated paper; cardboard, fiberboard
| Population by year (thousands of inhabitants) | |||||||
| 1959 | 16.3 | 1997 | 49.2 | 2008 | 42.2 | 2017 | 38.7 |
| 1970 | 34.2 | 1998 | 49.1 | 2010 | 41.9 | 2018 | 38.4 |
| 1979 | 47.8 | 2000 | 49.0 | 2011 | 40.6 | 2019 | 38.1 |
| 1986 | 50 | 2001 | 48.9 | 2012 | 40.3 | 2020 | 37.7 |
| 1989 | 50.2 | 2003 | 43.4 | 2013 | 39.9 | 2021 | 37.3 |
| 1992 | 50 | 2005 | 42.9 | 2014 | 39.6 | ||
| 1995 | 49.5 | 2006 | 42.5 | 2015 | 39.2 | ||
| 1996 | 49.4 | 2007 | 42.3 | 2016 | 38.9 | ||
Koryazhma is an old and small town
This is one of the ancient cities in the region, which was developed in the 16th century. There is a cellulose processing plant here, which is one of the main enterprises of the settlement. The population, according to 2021 data, was only 37 thousand inhabitants.
Negative dynamics have been observed since 1998. The city administration promises to correct the demographic situation. This locality plans to introduce an affordable housing program.